Network Protection👀
约 1042 个字 预计阅读时间 3 分钟
Firewall / IDS / IPS / HoneyPot👀
Honeywords👀
- Associate false passwords (honeywords) with each user’s account
- Attacker that steals (hashed) password file cannot distinguish from passwords from honeywords
- Attempted login using a honeyword sets off an alarm
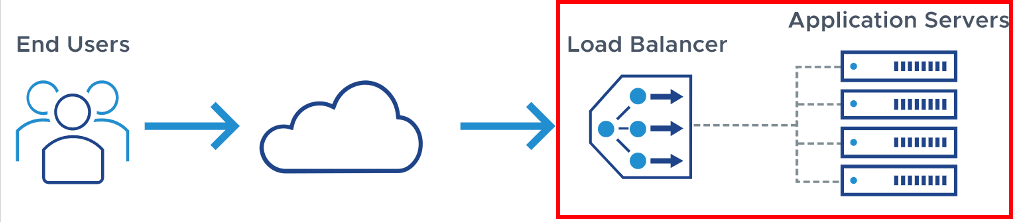
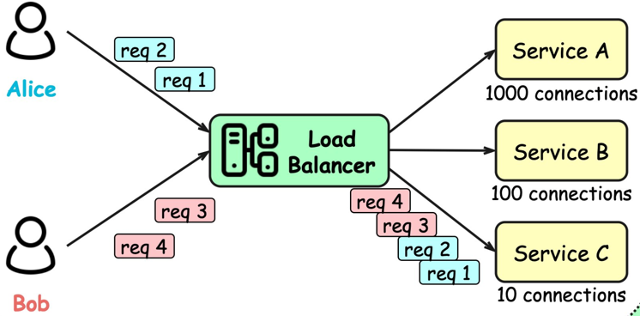
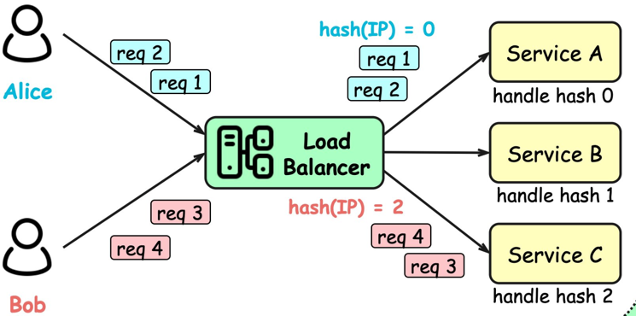
Load Balancing👀
- Distribute network traffic across multiple servers
- Mitigate single point of failure
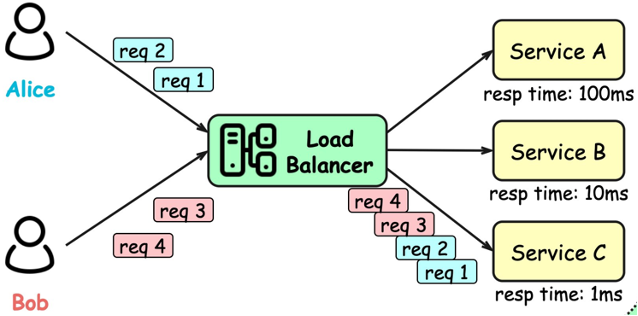
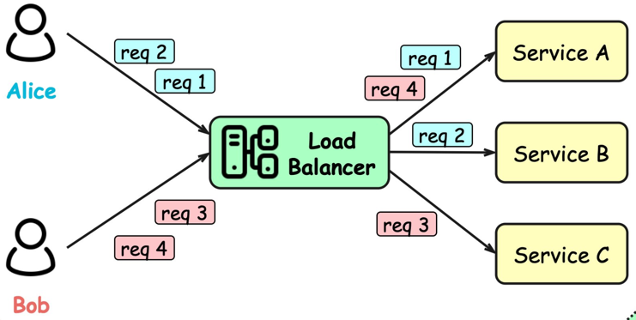
direct traffic to the server with the fewest active connections and the lowest average response time
Traffic Scrubbing👀
- Use a data cleansing service that analyzes traffic and filters malicious traffic
- Such service provider should be equipped with sufficient resources to sustain high volumetric floods
Once an attack is detected,
- redirect traffic to scrubbing service
- Analyze and filter malicious traffic
- Deliver clean traffic to network/user
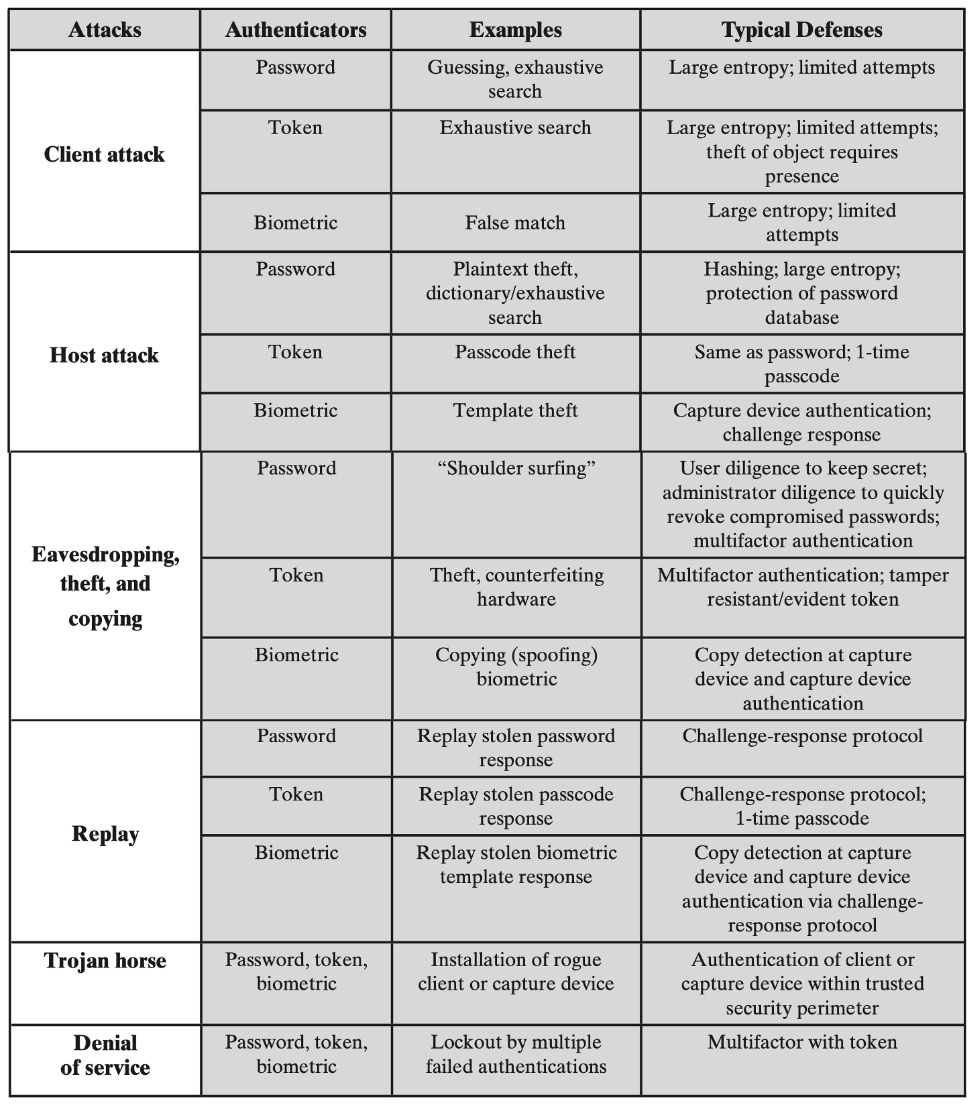
User Authentication👀
- The basis for most types of access control and for user accountability
- The process of verifying an identity claimed by or for a system entity
present an identifier to the security system
present or generate authenticaton information that corroborates the binding between the entity and identifier
Means of authentication👀
一些认证手段
- Information the user knows
- passwords, personal identification number (PIN), answers to prearranged questions
- Information the user possesses
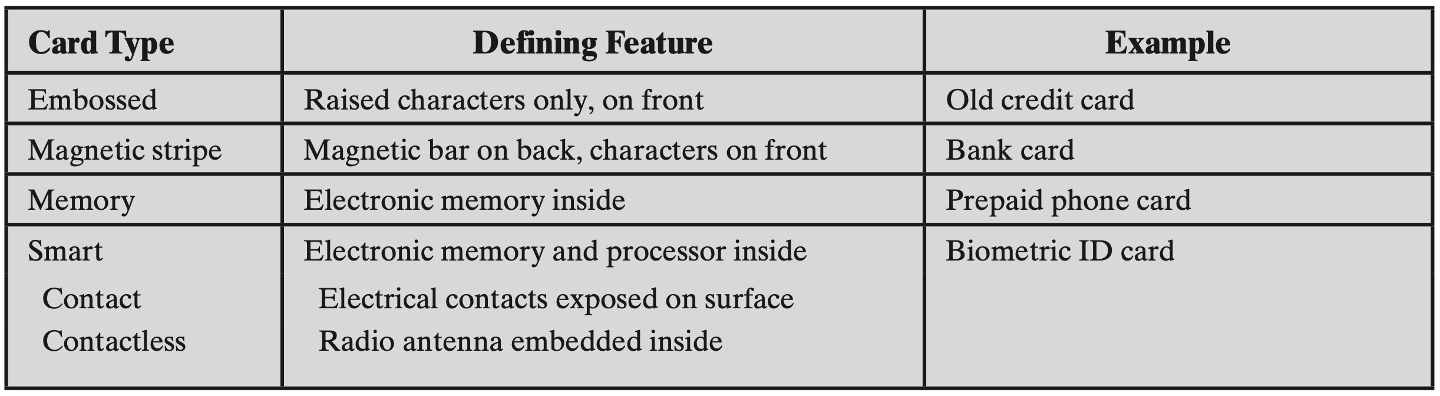
- electronic keycards, smart cards, physical keys
- Information the user is
- static biometrics: fingerprint, retina, face
- Information the user does
- dynamic biometrics: voice pattern, handwriting characteristics, typing rhythm
Password👀
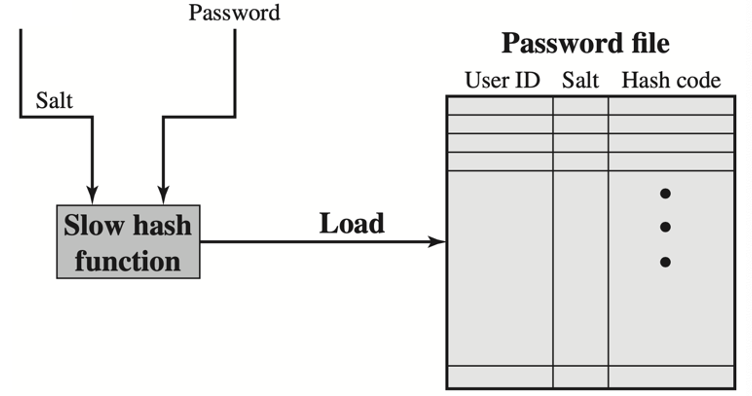
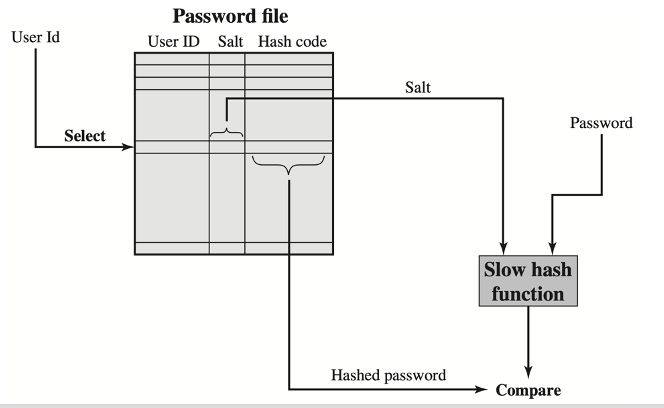
- A cryptographic salt is made up of random bits added to each password instance before its hashing.
- Salts create unique passwords (hash code) even in the instance of two users choosing the same passwords.
- Salts help us mitigate hash table attacks by forcing attackers to re-compute them using the salts for each user.
Salt Purpose
- Prevent duplicate passwords from being visible in the password file
- Greatly increase the difficulty of offline dictionary attacks
- Greatly increase the difficulty of finding out whether a person has used the same password on two or more systems
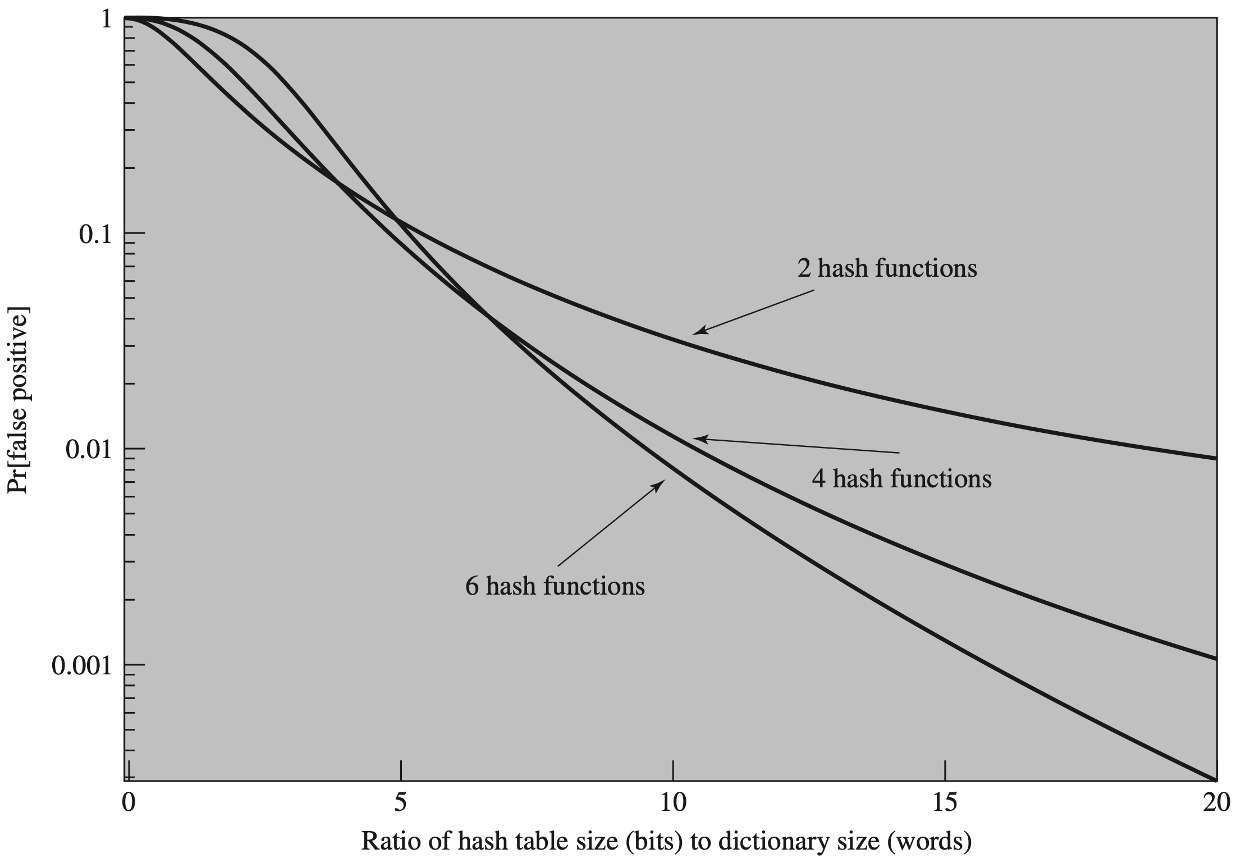
Bloom Filter
- 它实际上是一个很长的二进制向量和一系列随机映射函数。
- 布隆过滤器可以用于检索一个元素是否在一个集合中。
- 优点:
- 时间复杂度低,增加和查询元素的时间复杂为O(N),(N为哈希函数的个数,通常情况比较小)
- 保密性强,布隆过滤器不存储元素本身
- 存储空间小,如果允许存在一定的误判,布隆过滤器是非常节省空间的(相比其他数据结构如Set集合)
- 缺点:
- 有点一定的误判率,但是可以通过调整参数来降低
- 无法获取元素本身
- 很难删除元素
Quote
Biometric
Authenticate a user based on the user’s unique physical characteristics: facial characteristics; fingerprints; hand geometry; retinal pattern; iris; signature; voice
Access Control👀
Implement a security policy that specifies who or what (e.g., a process) may have access to each specific system resource and the type of access that is permitted in each instance
不同主体有不同的访问权限
Authorize a subject with some access right(s) for some object(s)
- Subject (Entity capable of accessing objects)
- Owner
- creator of a resource, system administrator, project leader, etc.
- Group
- a named group of users with shared access rights;
- a user may belong to multiple groups.
- World
- users other than owner and group
- Owner
- Object
- Resource to which access is controlled
- Entity used to contain and/or receive information
- Access Right
- Describe the way in which a subject may access an object
- Read, write, execute, delete, create, search…
DAC | Discretionary Access Control👀
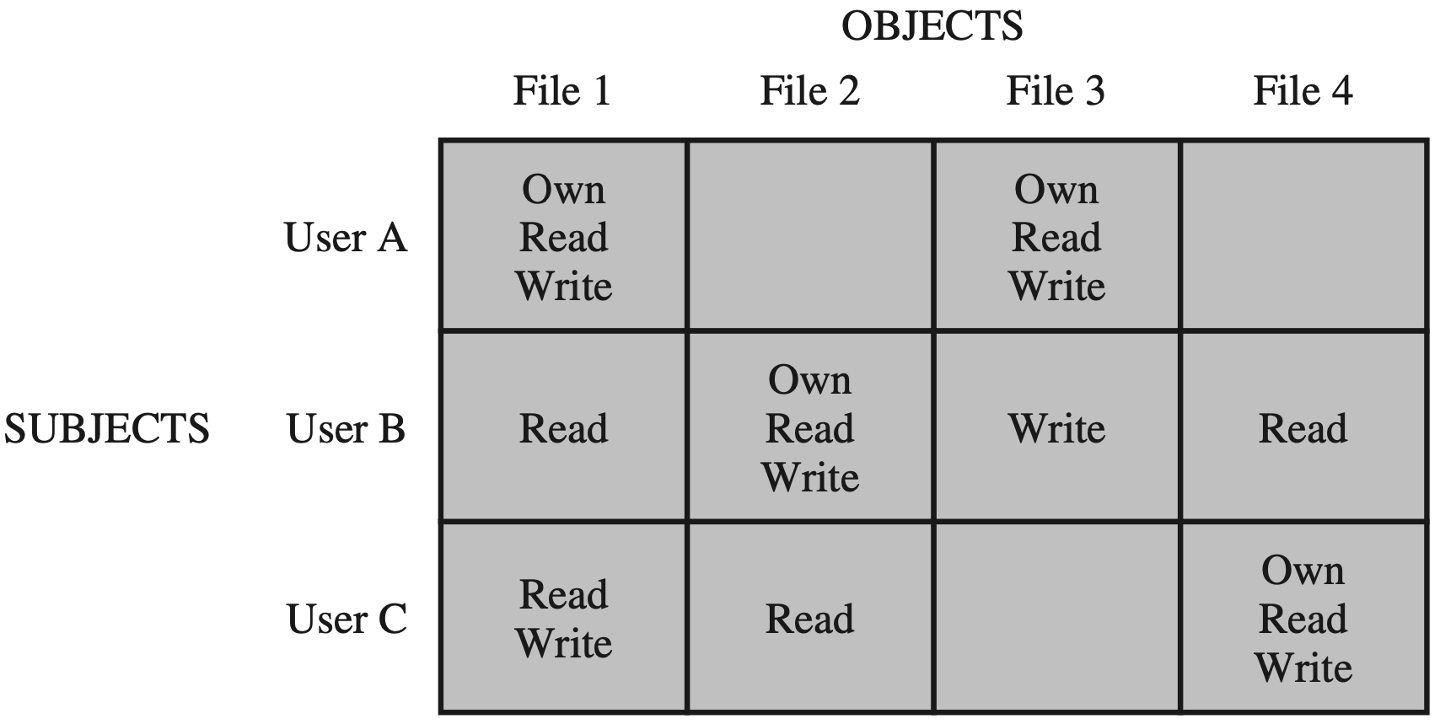
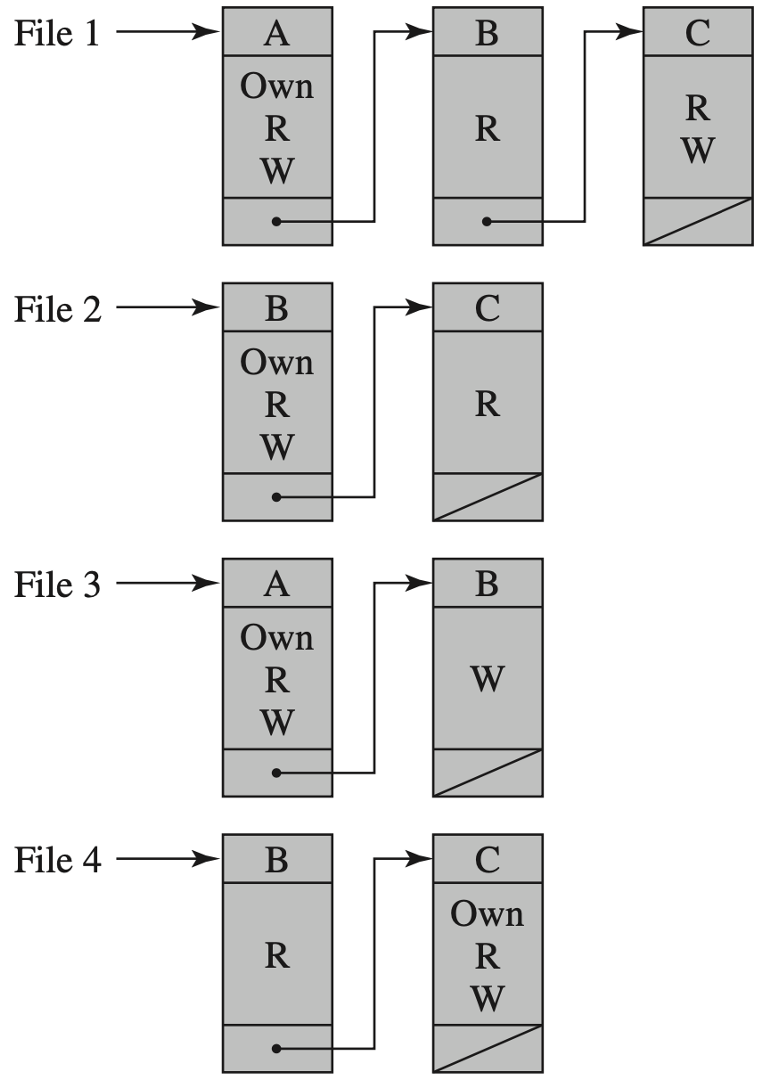
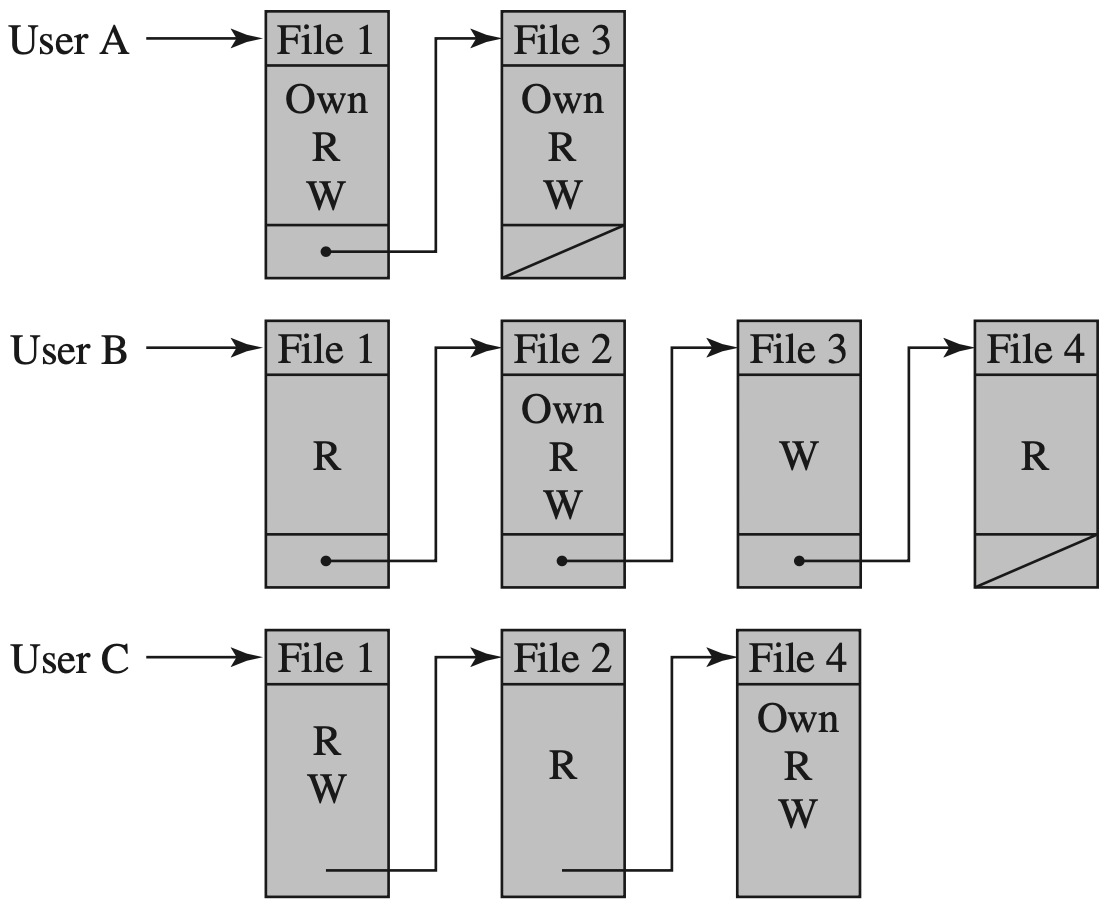
简单来说可以建立一个访问控制矩阵 (Access Matrix)
实现快速访问,但如果过于稀疏的话,会浪费空间
引入下面两种设计:
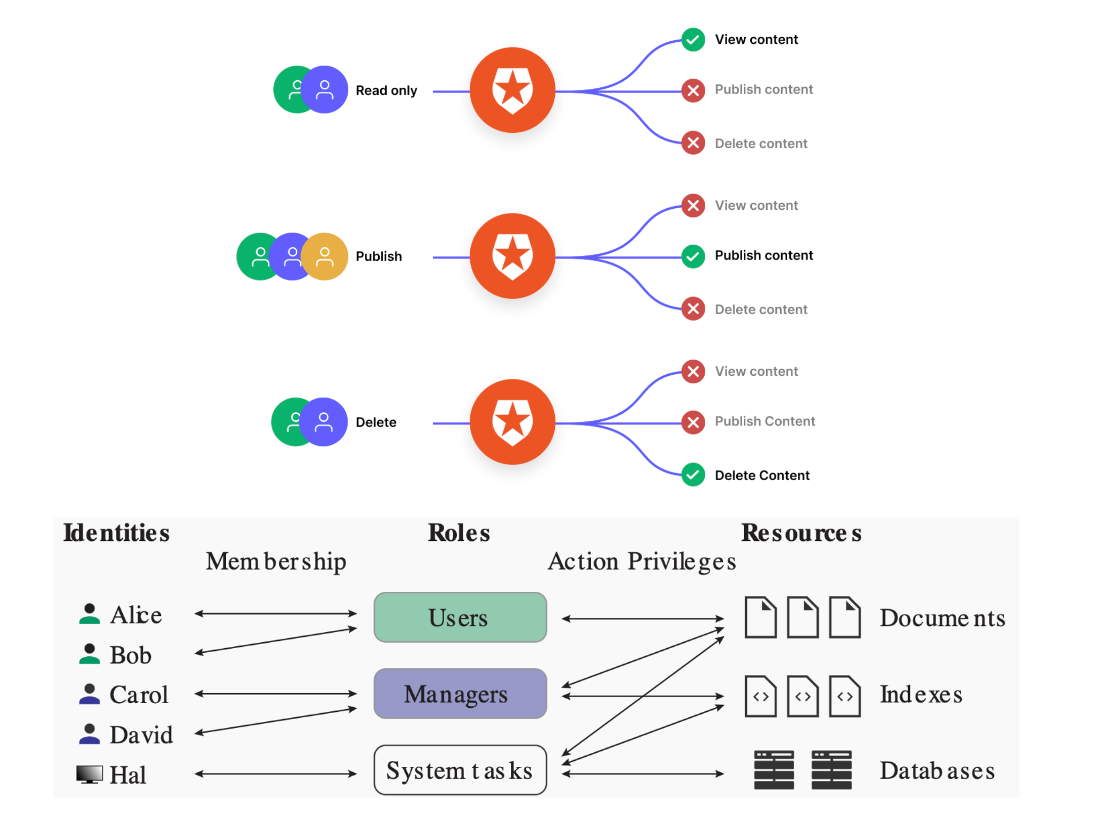
RBAC | Role-Based Access Control👀
- Assign users with different roles according to their responsibilities
- Check the roles that users assume in a system rather than the user’s identity
ABAC | Attribute-Based Access Control👀
Define authorizations that express conditions on properties of both the resource and the subject
基于实时的属性和使用场景划分用户对某资源的访问权限, 更灵活,前几种都是分配了访问权限之后就固定了
RBAC to ABAC
- roles can define privileges that can be dynamically determined based on any attribute of user/subject or data/object
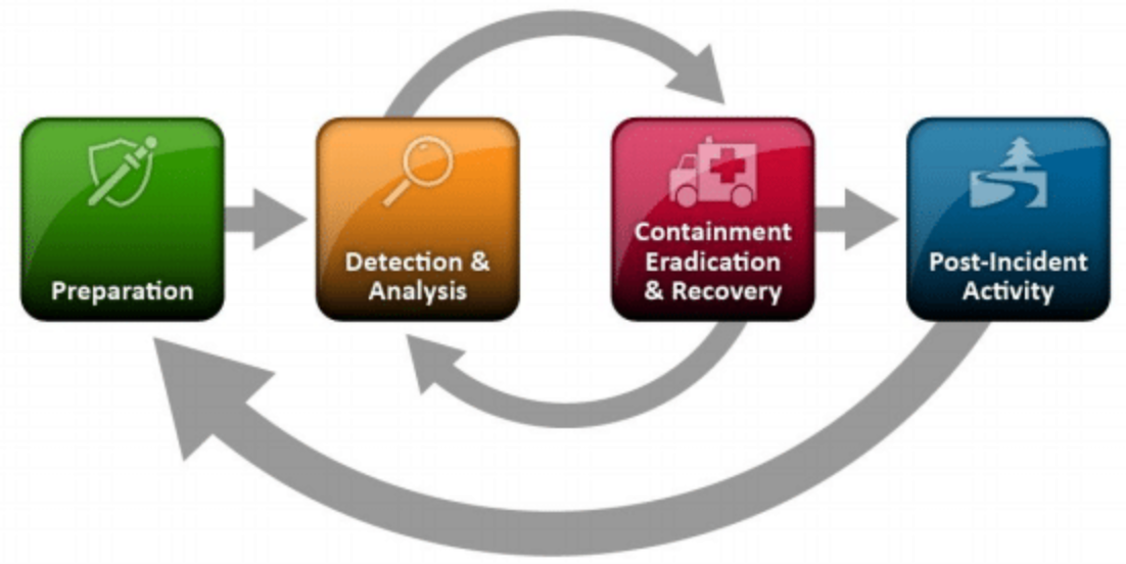
Incident Response👀
Cyclical activity featuring ongoing learning and advancements to discover how to best protect the organization | 周期性活动,不断学习和进步,以发现如何最好地保护组织
Four main stages: (在四个阶段中不断切换反复)
- preparation
- Set up baseline of normal activity. Determine which types of security events should be investigated
- detection/analysis
- Detect potential attack and further investigate if and how it deviates from normal behavior
- containment/eradication
- Identify and block attacking traffic; identify and remove attack related elements
- recovery
- Recover normal operations as quickly as possible, taking steps to prevent subsequent attacks
Incident Response Steps
- Assemble a team of experts
- Detect and ascertain the source
- Contrain and recover
- Assess damage and severity
- Begin the notification process
- Take actions for prevention
- …