Traffic Analysis👀
约 1409 个字 预计阅读时间 5 分钟
filter malicious traffic
Firewall👀
- Form a barrier through which the traffic going in each direction must pass | 双向流量都需要通过这个 barrier
- Use
firewall security policyto dictate which traffic is authorized to pass in each direction
Design Goals👀
- All traffic from inside to outside, and vice versa, must pass through the firewall.
- Only authorized traffic, as defined by the local security policy, will be allowed to pass.
- The firewall itself is immune to penetration.
Design Techniques👀
Service Control👀
determine service types that can be accessed (inbound or outbound)
- Filter traffic on the basis of IP address, protocol, or port number
- Provide proxy software that receives and interprets each service request before passing it on
- Host the server software itself, such as Web or Email service
Direction Control👀
determine the direction in which particular service requests may be initiated and allowed to flow through the firewall
User Control👀
control access to a service according to which user is attempting to access it
- Typically apply to local users
- Also apply to external users via secure authentication technology (e.g., IPsec Authentication Header)
Behavior Control👀
control how particular services are used
E.g.,
- filter E-mail to eliminate spam, or
- enable external access to only a portion of the information on a local Web server
Firewall Types👀
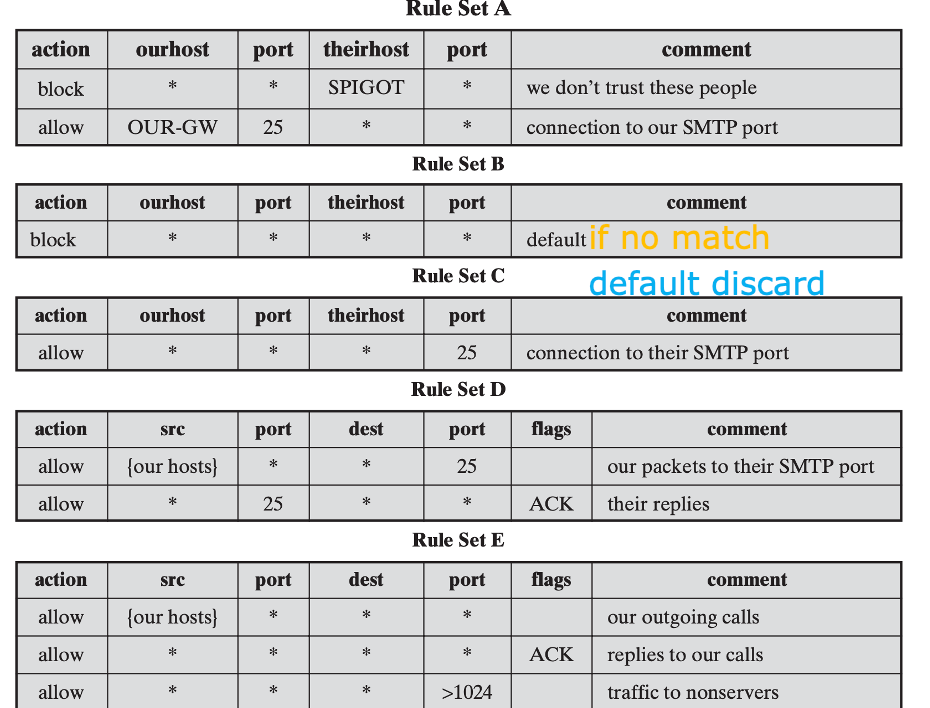
Packet Filtering Firewall👀
Apply a set of rules to each incoming and outgoing IP packet, Forward or discard the packet
- Make filtering decisions on an individual packet basis
- Consider no higher-layer context
- If no match, default discard, or default forward
Packet Filtering Firewall
- 对传输层进行过滤,firewall 充当 interface, 数据包头部会有
source IP/port,destination IP/port,protocol
- 通过检查数据包的头部信息,来决定是否允许数据包通过
Stateful Inspection Firewall👀
Both packets and their context are examined by the firewall
数据包和它们的上下文都由防火墙检查,也发生在传输层
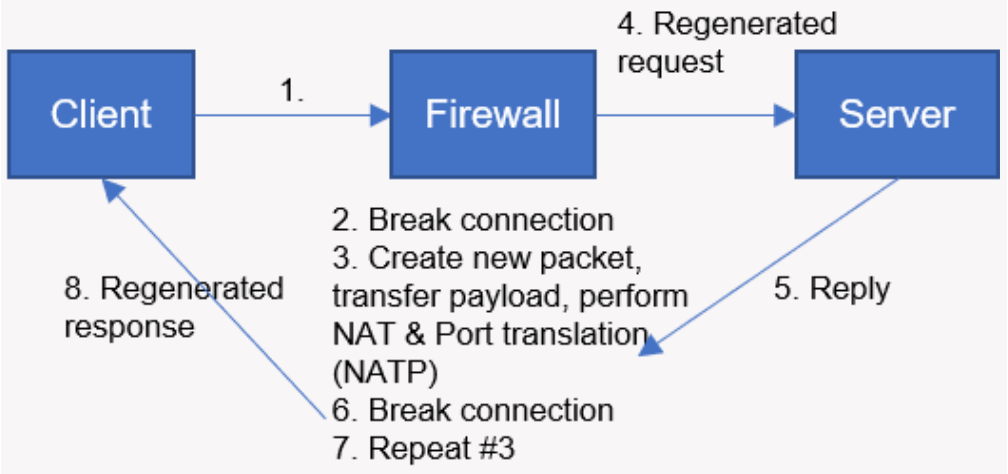
Application Proxy Firewall👀
- Application-Level Gateway | 应用层
- Act as a relay of application-level traffic
作为一个应用层的 relay,使得客户端和服务端从不直接交互,而是以防火墙作为代理,同时可以检查数据包的全部内容
more explanation
- An application-proxy firewall is a server program that understands the type of information being transmitted—for example, HTTP or FTP.
- It functions at a higher level in the protocol stack than do packet-filtering firewalls, thus providing more opportunities for the monitoring and control of accessibility
Circuit-Level Proxy Firewall👀
- Circuit-Level Gateway (还是在传输层)
- Act as a relay of TCP segments without examining the contents
- Set up two TCP connections instead
作为一个 transport layer 的 relay,代理主机和对方完成 TCP 连接建立;一旦建立连接后就正常转发,不检查内部内容。
Where Firewall Stand?👀
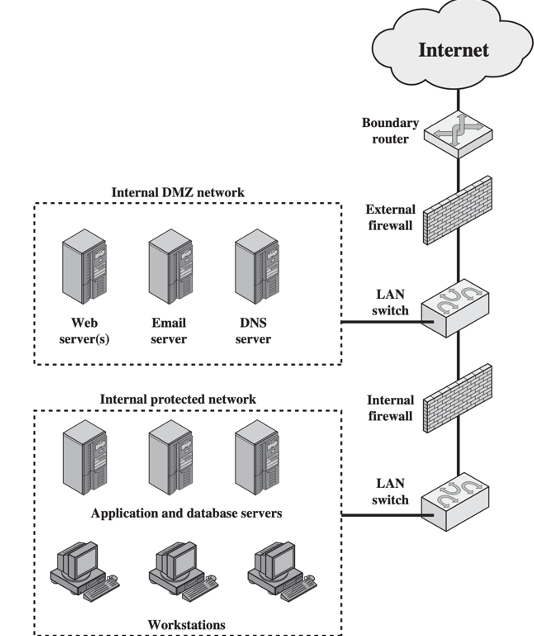
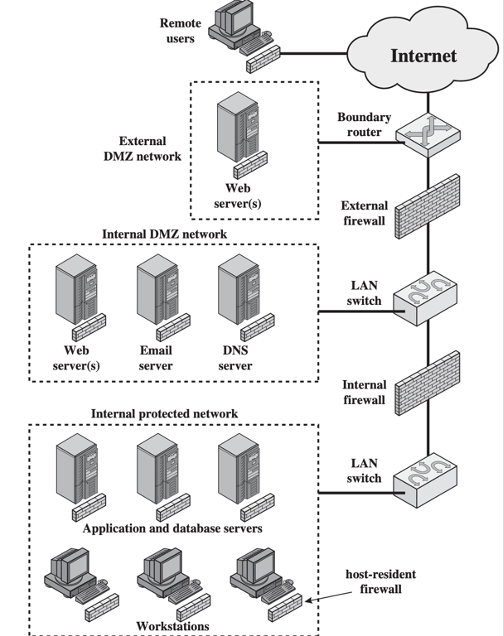
DMZ Networks👀
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone | 停火区)
- External Firewall
- provide access control and protection for DMZ systems consistent with their need for external connectivity
- Internal Firewall
- add more stringent filtering capability;
- protect internal network from attacks from DMZ and vice versa;
- protect internal networks from each other;
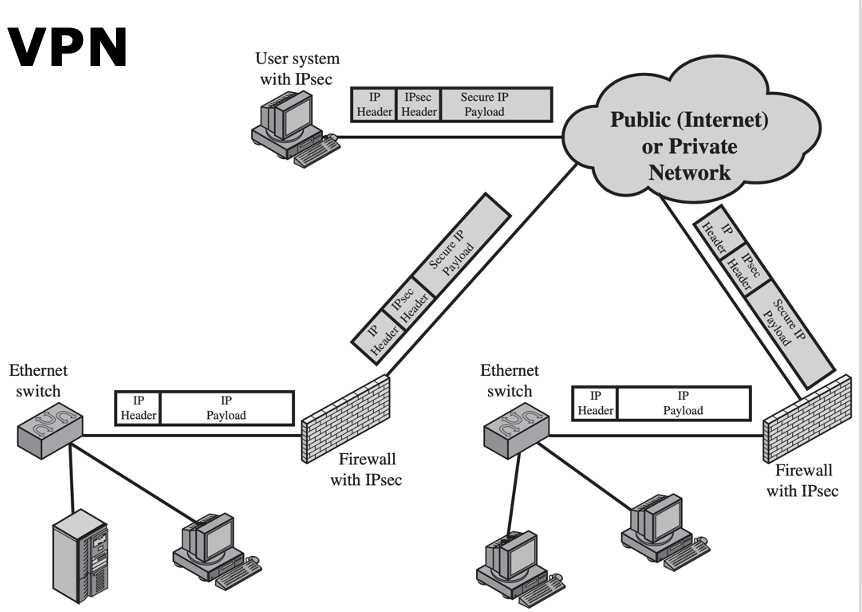
Virtual Private Networks👀
- Use encryption and authentication in the lower protocol layers to provide a secure connection through insecure Internet
- Cheaper than real private networks using private lines
- Common protocol in use: IPsec
Distributed Firewalls👀
- Stand-alone firewall devices + host-based firewalls work together under a central administrative control
IDS👀
traffic pattern learned?
individually secure packets yet collaboratively malicious (e.g. TCP SYN Flood)
IDS (Intrusion Detection System)
- Detect unusual patterns of activity or patterns of activity that are known to correlate with intrusions
- Provide early warning of an intrusion so that defensive action can be taken
Instruction Behavior Pattern👀
Info
- Hacker
- Select the target using IP lookup tools such as NSLookup, Dig, and others.
- Map network for accessible services using tools such as NMAP.
- Identify potentially vulnerable services (in this case, pcAnywhere)
- Brute force (guess) pcAnywhere password.
- Install remote administration tool called DameWare.
- Wait for administrator to log on and capture his password
- Use that password to access remainder of network.
- Criminal Enterprise
- Act quickly and precisely to make their activities harder to detect.
- Exploit perimeter through vulnerable ports.
- Use Trojan horses (hidden software) to leave back doors for reentry.
- Use sniffers to capture passwords.
- Do not stick around until noticed.
- Make few or no mistakes.
- Internet Threat
- Create network accounts for themselves and their friends.
- Access accounts and applications they wouldn’t normally use for their daily jobs.
- E-mail former and prospective employers.
- Conduct furtive instant-messaging chats.
- Visit Web sites that cater to disgruntled employees, such as f’dcompany.com.
- Perform large downloads and file copying
- Access the network during off hours.
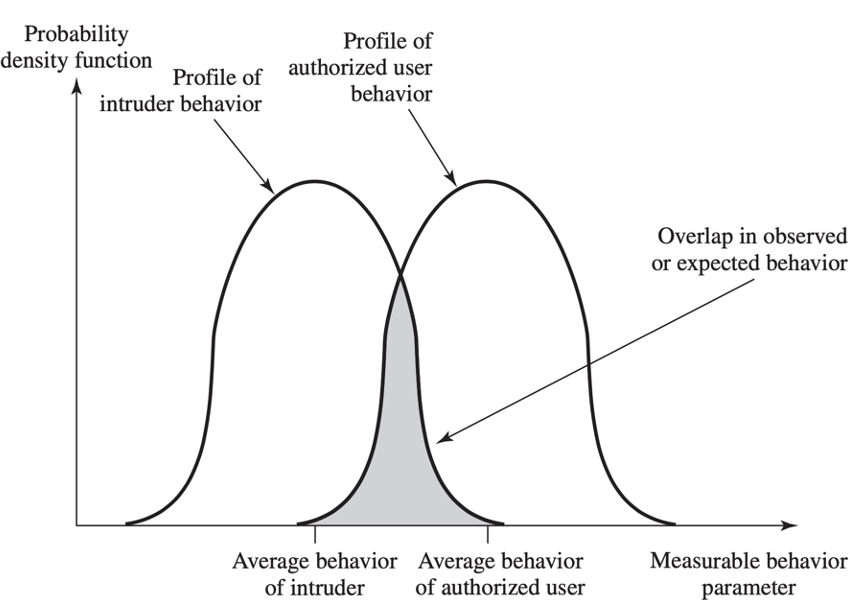
intruder behavior differs from that of a legitimate user in ways that can be quantified:
How to Detect Intrusion👀
- Audit Record
- Record ongoing activity of users
- Input records to IDS
- Native Audit Record
- use available accounting software in OS to collect user activity information;
- need no additional collection software;
- may not contain needed information or may not contain it in a convenient form;
- Detection-Specific Audit Record
- use a dedicated facility to generate audit records containing only required information for IDS;
- vender independent and portable;
- extra overhead
- Example fields - Subject, Action, Object, Exception Condition, Resource-Usage, Time-Stamp
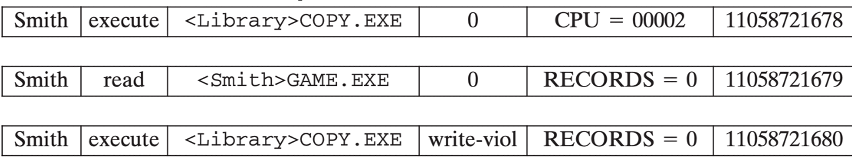
- Statistical Anomaly Detection
- Threshold detection
- count the number of occurences of a specific event type over an interval of time, detect an intrusion if the number exceeds a reasonable number (如果超过合理数量,则报告入侵)
- Profile-based detection (Signature)
- characterize past behavior of some user(s), detect an intrusion if a significant deviation occurs (如果发生重大偏差,报告入侵)
- Threshold detection
- Rule-Based Detection
- Detect intrusion by observing events in the system and applying a set of rules that lead to a decision regarding whether a given pattern of activity is suspicious or not
- Analyze historical audit records to identify usage patterns and generate rules that describe those patterns
- e.g., aggregated traffic volume exceeds a threshold
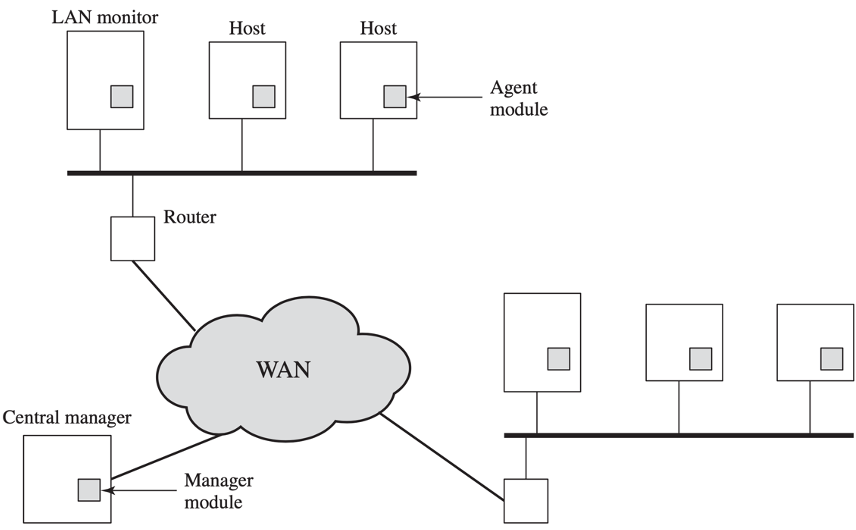
Distributed IDS👀
- operate as a background process on a monitored system;
- collect data on security-related events on the host and transmit to central manager;
- operate the same as host agent module except that it analyzes LAN traffic and reports to central manager;
- receive reports from LAN monitor and host agents, process and correlate these report to detect intrusion;
how to profile attack more?
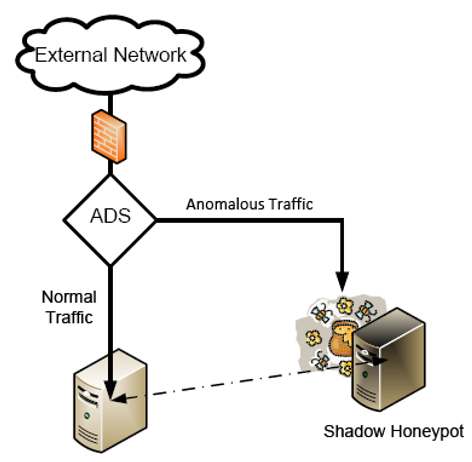
Honeypot👀
- Decoy systems designed to lure a potential attacker away from critical systems
- Collect information about the attacker’s activity
- Encourage the attacker to stay on the system long enough for administrators to respond
ADS (Active Defense System)
how accurate is IDS?
IDS Detection Accuracy👀
- Detection rate / True Positive Rate (TP)
- given that there is an intrusion, how likely will the IDS correctly output an alert
- False Negative Rate: FN = 1 - TP
- False Alarm / False Positive Rate (FP)
- given that there is no intrusion, how likely is the IDS to falsely output an alert
- True Negative Rate: TN = 1 - FP
IDS vs Firewall
- Firewall supports active filtering
- IDS provides only passive monitoring
IPS👀
- Intrusion Prevention System
- an extension of IDS to attempt to block or prevent detected malicious activity
- Host-based, network-based, or distributed
- Anomaly detection to identify behavior different from legitimate users
- Signature/heuristic detection to identify malicious behavior
Advanced Traffic Analysis👀
Pattern Correlation
- Pair users of secure messaging applications
- Secure messaging applications’ traffic features
- event-based algorithm
- shape-based algorithm
- Machine learning
- Deep learning
but Attacker can hide traffic patterns:
- Traffic Obfuscation | 混淆
- Encrypt traffic to hide payloads
- Use proxy to hide entire packets
- Introduce noise traffic to hide patterns
- e.g. ditto:
- Obfuscate packet size by padding
- Obfuscate transmission interval by dummy packets
how to detect evasion?
more advanced analysis:
Active Probing
- Suspicious of a host using a certain software (e.g., cryptomining)?
- Send a probe (e.g., to a specific port) under the protocol of the software
- See if the probed host responds as expected
大意就是主动发一个探测器过去,看看对面反应正不正常