DDos👀
约 6170 个字 预计阅读时间 21 分钟
Dos | Denial of Service👀
- DoS (Denial of Service) 攻击是一种网络攻击,目的是使目标系统或网络资源无法提供服务
- 即控制一个机器,向目标机器发送大量的请求以 overload 目标机器,使其无法处理合理的请求(e.g., 卖当劳派大量自家员工去坑德基点东西,但是不买单且处处刁难,使得坑德基无法正常服务真正的顾客)
- defence: block the attacking device
DDoS | Distributed Denial of Service👀
在 DoS 攻击中,攻击者使用单个系统向目标系统发送大量请求。在 DDoS 攻击中,攻击者使用多个系统向目标系统发送大量请求。使得仅仅通过阻止攻击者的 IP 地址无法阻止攻击。
Symmetric DDoS Attack👀
the attacker requires a substantial amount of traffic to succeed.
Ping Flood👀
Ping Flood
- Ping Flood 是一种网络攻击,它利用了
ping命令来向目标主机发送大量的ping请求, 使目标主机不断地响应请求,从而导致网络拥塞和服务质量下降、使目标主机过载或崩溃。 - Ping Flood 攻击通常是 DDoS 的一种形式.
1) Attack principle:
简言之:saturate the target device’s capacity by sending many ICMP echo request packets
- Exploit the ICMP protocol
- both incoming ICMP Echo Request and outgoing ICMP Echo Reply consume bandwidth;
- overwhelm the target device’s ability to respond to a high number of requests and/or overload the network connection with bogus traffic | 压制目标设备响应大量请求的能力,and/or 使网络连接超负荷运行假流量
- attacker sends a large number of ICMP echo request packets & target server sends an ICMP echo reply packet to each requesting device’s IP address as a response
2) Ping Flood DDoS 形式可以分解为两个重复的步骤:
- The attacker sends many ICMP echo request packets to the targeted server using multiple devices.
- The targeted server then sends an ICMP echo reply packet to each requesting device’s IP address as a response.
3) 解决方法
- disable the ICMP functionality of the targeted device (make the device unresponsive to ping requests and traceroute requests)
- 虽然很有效,但后果是所有涉及 ICMP 的网络活动都被禁用,包括网络诊断工具
ping和traceroute。
more about Ping Flood
- 在 Ping Flood 攻击中使用的互联网控制信息协议 (ICMP) 是网络设备用于通信的互联网层协议。
- 网络诊断工具
traceroute和ping都使用 ICMP 操作。通常情况下, ICMP 回波请求和回波回复信息用于 Ping 网络设备,目的是诊断设备的健康状况和连接性,以及发送者和设备之间的连接。 -
一个 ICMP 请求需要一些服务器资源来处理每个请求和发送响应。该请求还需要传入信息(回音请求)和传出响应(回音响应)的带宽。
-
历史上,attackers 通常会伪造一个假的ip地址,以掩盖发送设备
- 在现代僵尸网络攻击中,恶意行为者很少认为有必要掩盖僵尸的 IP, 而是依靠一个由未被欺骗的僵尸组成的大型网络来使目标的容量饱和
TCP SYN Flood👀
TCP SYN Flood
- TCP SYN Flood 是一种 DDoS 攻击,它利用了 TCP 协议的三次握手过程中的漏洞,通过向目标服务器发送大量的 TCP 连接请求,使目标服务器的资源耗尽,无法处理合理的请求。
攻击原理
- attacker 使用僵尸网络发送大量的 TCP 连接请求 (向目标服务器发送 TCP SYN 数据包,但不完成 TCP 三次握手过程)
- 目标服务器收到 SYN 数据包后,会响应一个 SYN+ACK 数据包,等待客户端的 ACK 数据包。但由于 attacker 不会发送 ACK 数据包,因此目标服务器会一直等待,直到超时。
- 服务器必须维护每个未完成的连接请求的状态,直到超时1或关闭。即服务器会为每一个 SYN 数据包分配一些资源,并将其放入 SYN queue/ SYN backlog 中,等待客户端的 ACK 数据包。但这个队列的容量是有限的 (commonly set as 128 by default on some Linux systems), 一旦队列满了,服务器将不再接受新的连接请求。
- 假设服务器的 SYN backlog 队列容量为 128,超时时间设置为 3 mins。攻击者每 3 分钟发送 128 个 SYN 数据包,服务器将一直等待,直到超时,而不会接受新的合法请求。
Single machine:
- SYN packets with random source IP addresses
- Fill up backlog queue on server
- No further connections possible
1) Attack principle:
- server commits resources (memory) before confirming identify of client (when client responds)
2) TCP SYN Flood 的改进: IP Spoofing : Craft SYN packets from randomly forged IP address
- SYN packets with random source IP addresses
- Fill up backlog queue on server
- No further connections possible
For such random IP addresses, after they receive SYN ACK packets from the server, they may simply discard them as these IP addresses have not sent SYN requests at all
3) Solution:
- increase backlog queue size
- but attacker can sends more SYN packets!
- decrease timeout
- but interrupt normal service requests!
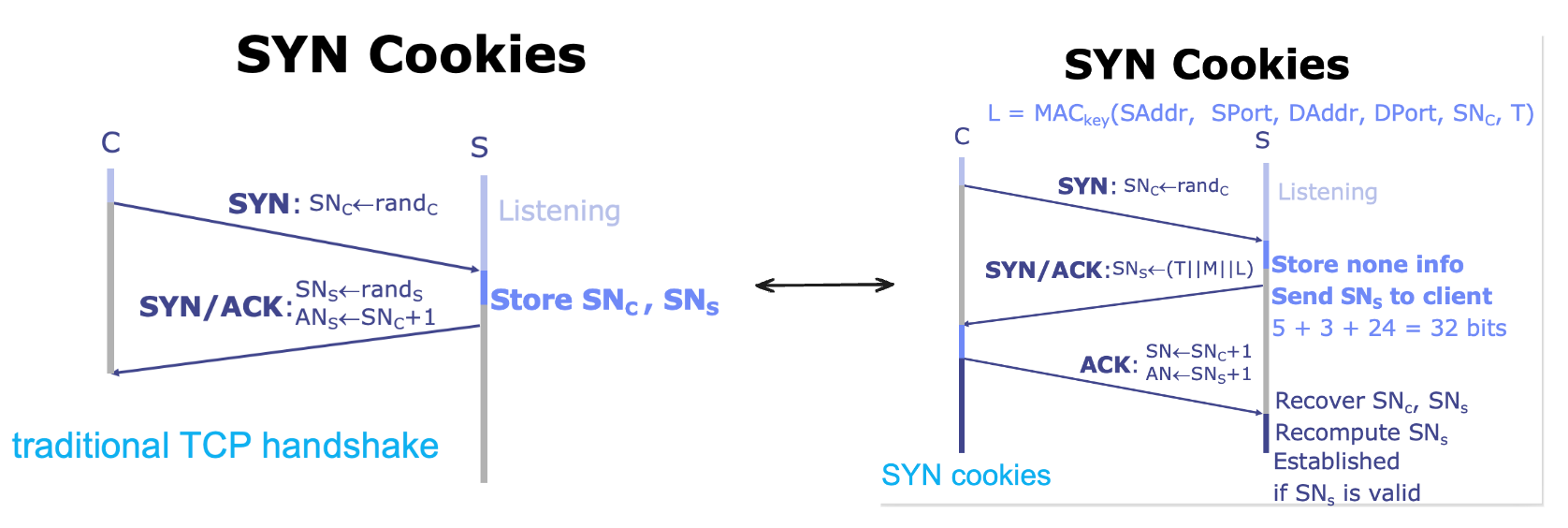
- SYN Cookies
- Goal: avoid state storage on server until 3-way handshake completes
- Idea:
- server sends necessary states to client along with SYN-ACK;
- client sends these states back to server along with ACK;
- 通过 SYN Cookies, server 可以在未验证每个连接请求之前不为其分配资源,从而免受 TCP SYN Flood 攻击的影响(但持续计算验证 SYN 也很消耗资源)
SYN Cookies
- 在 client 发送给 server 的 SYN 包后,相比之前的 TCP handshake, server 不再保存 client 的 SNC 包,而是将 client 的信息加密后发送给 client 自己的 SNS 包,其中 SNS = (T || M || L) (Total 32 bits)
- T: 5-bit timestamp time() logically right-shifted 6 positions; 64-second resolution
- M: 3-bit MSS (maximum segment size)
- L: 24-bit keyed hash, L = MACkey (SAddr, SPort, DAddr, DPort, SNC, T)
- server 收到 client 发回的 ack 包后,复原 SNC 和 SNS,之后核验 SNS 即可判断是否是合法的 client
4) TCP SYN Flood Backscatter: 指 server 接收到 Spoofed IP 的 SYN 后发回的 SYN + ACK 包
- backscatter packets can be used for detecting DDoS attacks
- Detection Principle: Since syn flood uses forged source IP, then responses to those forged IPs get no further responses
Asymmetric DDoS Attack👀
A relatively small number or low levels of resources are required by an attacker to cause a significantly great number or higher level of target resources to malfunction or fail.
Some Typical Examples👀
1) Smurf Attack
Smurf Attack
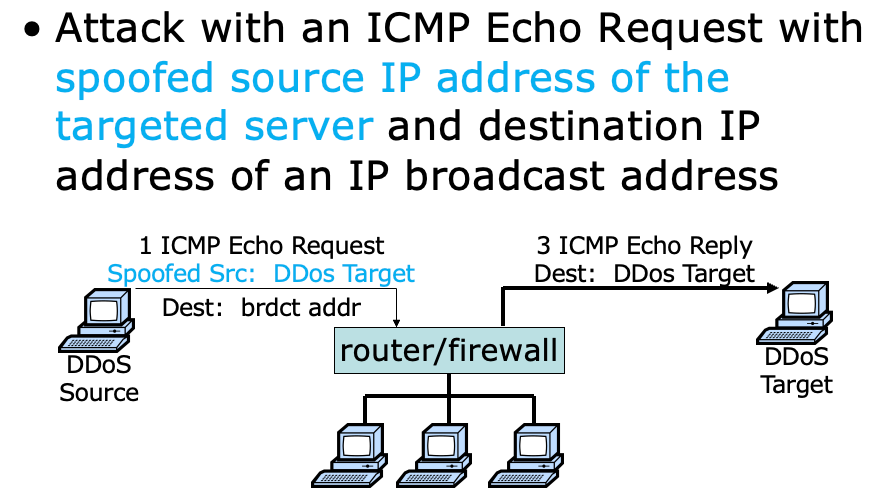
- 又称 Smurf Dos 攻击,是一种早期的网络攻击方式,利用了 ICMP 协议的 “广播地址” 功能
- 攻击者伪造目标主机的 IP 地址,向网络中的广播地址发送 ICMP Echo 请求,网络中的所有主机都会响应这个请求,从而使得目标主机被大量的 ICMP Echo 响应包淹没
- Smurf Attack 通常是 DDos 的一种形式,可以使用多个网络节点进一步增强攻击强度和持续时间
- 特点:
- Amplify the effect of ping flood
- Exploit IP broadcast address
- Forward the single ICMP Echo Request to any other hosts in the same network
- Each host responds with an ICMP Echo Reply
- 1 request but many replies
- 解决方法:
- Disable IP broadcast addresses on router and firewall (即禁用子网的 broadcast 功能)
- Reject external packets to broadcast addresses (即拒绝外来的广播地址的请求)
How a Smurf Attack works:
- First the Smurf malware builds a spoofed packet that has its source address set to the real IP address of the targeted victim.
- The packet is then sent to an IP broadcast address of a router or firewall, which in turn sends requests to every host device address inside the broadcasting network, increasing the number of requests by the number of networked devices on the network.
- Each device inside the network receives the request from the broadcaster and then responds to the spoofed address of the target with an ICMP Echo Reply packet.
- The target victim then receives a deluge of ICMP Echo Reply packets, potentially becoming overwhelmed and resulting in denial-of-service to legitimate traffic.
2) DNS Amplification Attack
DNS Amplification Attack
- DNS Amplification Attack 是一种 DDoS 攻击,它利用了开放的 DNS 递归解析器来放大攻击流量,使目标服务器被大量的 DNS 响应包淹没
- 攻击者伪造目标主机的 IP 地址,向开放的 DNS 递归解析器发送大量 DNS 查询请求,递归解析器会返回大量的 DNS 响应包给目标主机,从而使得目标主机被大量的 DNS 响应包淹没
- 攻击者利用 DNS 查询特性,构造一个较小的查询请求,但会返回一个较大的 DNS 响应包,这种方式可以将攻击流量放大数倍
- 特点:
- 利用 open DNS resolvers (互联网公开、任何用户均可访问的 DNS resolver)
- 利用
ANY类型的 DNS 查询,可以获取给定名字的所有类型的信息 - Attack with an ANY-type DNS query with spoofed source IP address of the targeted server
- Amplify the effect of DNS query
- 1 request but many reponses
- EDNS: Extension Mechanisms for DNS sends DNS data in larger UDP packets (e.g. 60 bytes query, 3000 bytes response)
- Extension mechanism for DNS (EDNS, or EDNS(0)) gives us a mechanism to send DNS data in larger packets over UDP.
- 解决:
- reduce the number of open resolvers
- source IP verification - stop spoofed packets leaving network (这需要 ISP 来实现)
一个 DNS 扩增
A DNS amplification can be broken down into four steps:
- The attacker uses a compromised endpoint to send UDP packets with spoofed IP addresses to a DNS recursor. The spoofed address on the packets points to the real IP address of the victim.
- Each one of the UDP packets makes a request to a DNS resolver, often passing an argument such as “ANY” in order to receive the largest response possible.
- After receiving the requests, the DNS resolver, which is trying to be helpful by responding, sends a large response to the spoofed IP address.
- The IP address of the target receives the response and the surrounding network infrastructure becomes overwhelmed with the deluge of traffic, resulting in a denial-of-service.
3) NTP Amplification Attack
NTP Amplification Attack
- 和 DNS Amplification Attack 类似,NTP Amplification Attack 也是一种 DDoS 攻击,它利用了开放的 NTP 服务器来放大攻击流量,使目标服务器被大量的 NTP 响应包淹没
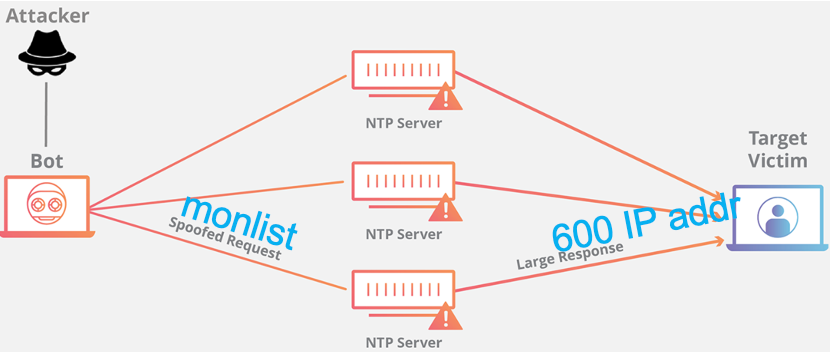
- 利用一些 NTP 服务器上启用的
monlist命令,攻击者可以成倍放大攻击流量,该命令在旧设备上默认启用,并使用向 NTP 服务器发出请求的最后 600 个源 IP 地址进行响应。来自内存中有 600 个地址的服务器的monlist请求将比初始请求大 206 倍。这意味着一个拥有 1GB 互联网流量的攻击者可以进行 200+ GB 的攻击 —> 由此导致的攻击流量大幅增加。
网络时间协议
- NTP (Network Time Protocol) 是一种用于同步计算机时钟的协议,它可以使计算机的时钟与全球标准时间同步,以确保计算机的时钟准确无误。
- NTP 的
monlist命令可以返回 NTP 服务器的监控信息,这个信息包含了最近的 600 个客户端的 IP 地址,这个信息可以被利用来放大攻击流量
- 特点:
- 利用 NTP servers
- 利用
monlistcommand - spoofed source IP address of the targeted server
- Amplify the effect of NTP query
- 1 query but a large reponses
- 解决:
- reduce the number of NTP servers that support monlist;
- source IP verification - stop spoofed packets leaving network (这需要 ISP 来实现)
一个 NTP 扩增
A NTP amplification can be broken down into four steps:
- The attacker uses a botnet to send UDP packets with spoofed IP addresses to a NTP server which has its monlist command enabled. The spoofed IP address on each packet points to the real IP address of the victim.
- Each UDP packet makes a request to the NTP server using its monlist command, resulting in a large response.
- The server then responds to the spoofed address with the resulting data.
- The IP address of the target receives the response and the surrounding network infrastructure becomes overwhelmed with the deluge of traffic, resulting in a denial-of-service.
4) Memcached Attack
Memcached Attack
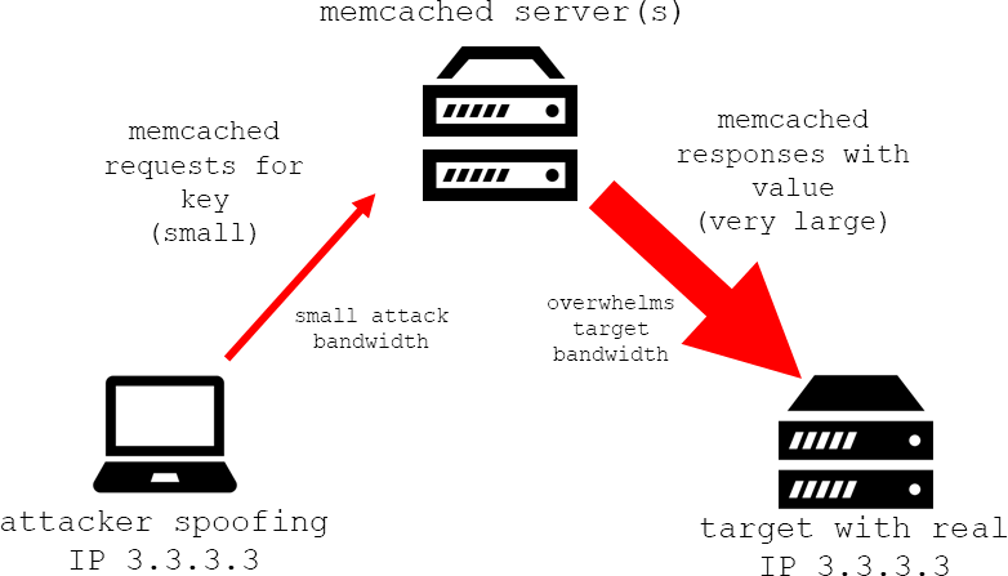
与所有 DDoS 放大攻击类似,利用了开放的 Memcached 服务器来放大攻击流量,使目标服务器被大量的 Memcached 响应包淹没
- Memcached 服务器是一种缓存数据的开源软件,可以用于提高 Web 应用程序的性能和响应速度。
-
Memcached 服务使用 UDP,因此发送前并不需要握手(前面几个也一样)。攻击者预先加载一些信息,然后伪装成 victim 向 server 请求。
-
特点:
- 利用 Memcached servers
- 利用 memcached request (triggers a response with a large volume of data to target)
- Attack principle:
- preload large data to Memcached server
- spoof request to preloaded data from target
- 解决:
- disable UDP on Memcached server
- firewall Memcached server
- source IP verification
flush_allcommand to Memcached server
一个 Memcached 攻击
A Memcached amplification can be broken down into four steps:
- An attacker implants a large payload* of data on an exposed memcached server.
- Next the attacker spoofs an HTTP GET request with the IP address of the targeted victim.
- The vulnerable memcached server that receives the request, which is trying to be helpful by responding, sends a large response to the target.
- The targeted server or its surrounding infrastructure is unable to process the large amount of data sent from the memcached server, resulting in overload and denial-of-service to legitimate requests.
5) SSDP Attack
- 特点:
- 利用 SSDP (Simple Service Discovery Protocol)
- 利用 UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) 网络协议
SSDP 攻击是一种利用 UPnP 协议的漏洞进行攻击的方式。UPnP 是一种网络协议,它允许设备自动发现并配置其他设备,从而实现设备的自动化交互。SSDP 是 UPnP 协议中的一个重要组成部分,它通过 UDP 广播的方式,在网络上发现和识别其他设备
-
Attack principle:
- the attacker conducts a scan looking for plug-and-play devices that can be utilized as amplification factors
- as the attacker discovers networked devices, they create a list of all the devices that respond
- the attacker creates a UDP packet with the spoofed IP address of the targeted victim
- the attacker then uses a botnet to send a spoofed discovery packet to each plug-and-play device with a request for as much data as possible by setting certain flags, specifically
ssdp:rootdeviceorssdp:all - as a result, each device will send a reply to the targeted victim with an amount of data up to about 30 times larger than the attacker’s request
- the target then receives a large volume of traffic from all the devices and becomes overwhelmed, potentially resulting in denial-of-service to legitimate traffic
-
解决:block incoming UDP traffic on port 1900 at the firewall
Asymmetric DDoS Attack (Computation Resource)👀
computation asymmetry
server costs more computation resources than attacker for a service request
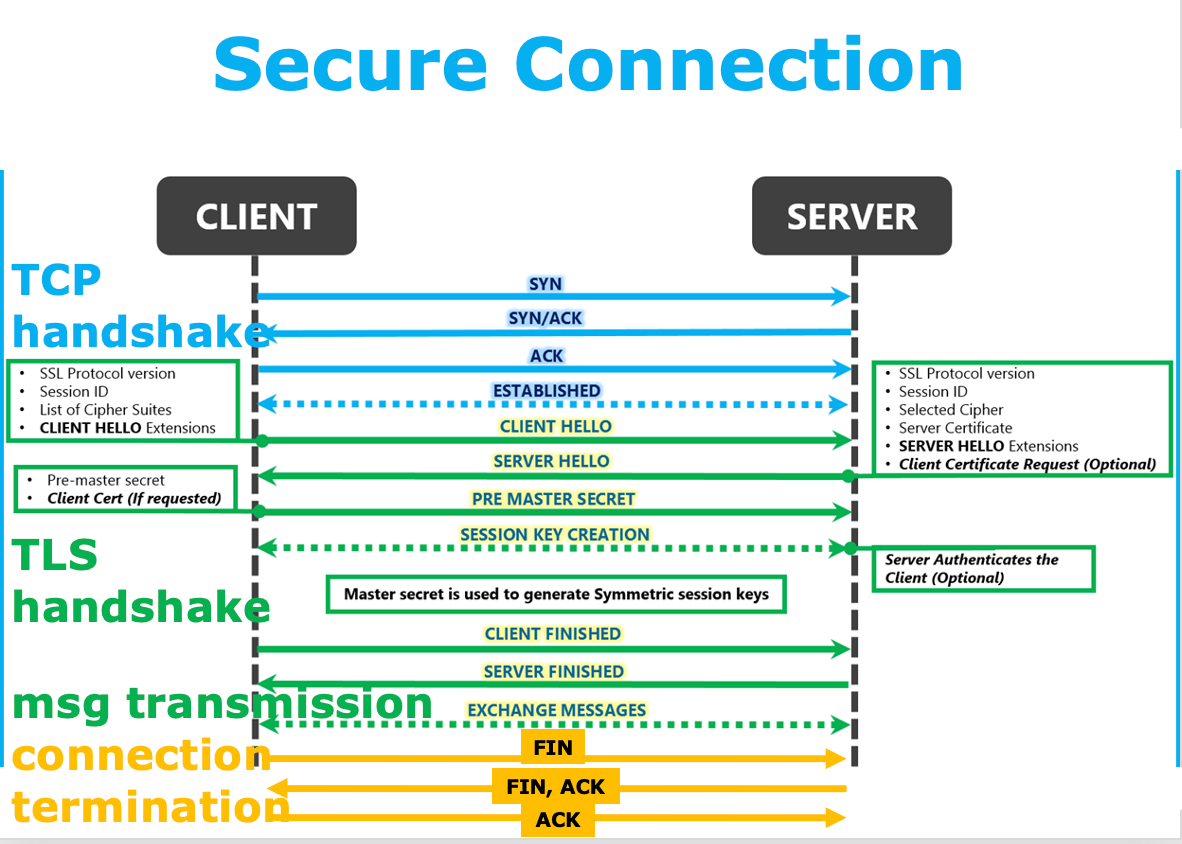
1) SSL/TLS Handshake
SSL/TLS
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) 和 TLS (Transport Layer Security) 是一种用于保护网络通信的协议,它们使用加密技术来确保数据在网络上的安全传输。SSL 是 TLS 的前身,TLS 是 SSL 的升级版。
- SSL/TLS 协议主要通过公开密钥加密技术 (Public Key Cryptography) 和 对称密钥加密技术 (Symmetric Key Cryptography) 来保护数据的机密性和完整性。
- SSL/TLS 握手期间,服务器和客户端需要进行多次通信,进行加密解密操作,这些操作会消耗服务器的大量计算资源。攻击者可以利用这一点,通过发送大量的 SSL/TLS 握手请求来耗尽服务器的计算资源
- Attack principle:
- Exploit SSL/TLS handshake requests to drain server resources
- RSA-enc speed \(\approx\) 10 \(\times\) RSA-dec speed
- Single machine can bring down 10 web servers
SSL Flood 或 SSL Renegotiation Attack 会利用服务器端协商安全 TLS 连接所需的处理能力。它要么向服务器发送大量垃圾数据,要么不断要求重新协商连接,从而使服务器资源超出极限,导致服务器脱机。
- 解决:
- 限制来自同一 IP 地址的请求
- 使用防火墙过滤器来阻止恶意流量
- 使用 SSL 加速器来提高服务器的处理能力
- 使用负载均衡器来分散流量
- 还可对系统进行优化,以提高其处理能力,如增加 CPU、内存等
2) HTTP Flood
HTTP Flood
- HTTP Flood 是一种 DDoS 攻击,它利用了 HTTP 协议的漏洞,如 HTTP 请求中的虚假信息、HTTP 请求中的合法信息超过服务器的处理能力等
- 攻击者通过大量的 HTTP 请求向目标服务器发送大量无效请求,从而耗尽服务器的资源,使目标服务器无法处理合法的请求
No IP Spoofing
- 不使用 IP Spoofing
- 因 HTTP Flood 需要 TLS,TLS 需要保证返回的 source IP 是自己的 IP
- Command attackers to:
- Complete the real TCP connection
- Complete the real TLS handshake
- Get/POST large image or other content
HTTP attack
- multiple computers or other devices are coordinated to send multiple requests for images, files, or some other asset from a targeted server.
- When the target is inundated with incoming requests and responses, denial-of-service will occur to additional requests from legitimate traffic sources.
- typically when a form is submitted on a website, the server must handle the incoming request and push the data into a persistence layer, most often a database.
- The process of handling the form data and running the necessary database commands is relatively intensive compared to the amount of processing power and bandwidth required to send the POST request.
- 这种攻击利用了相对资源消耗的差异,直接向目标服务器发送大量 POST 请求,直到服务器容量饱和并出现拒绝服务。
- 解决:
- block or rate limit attacking source
- Rate control against large volume of traffic that occupies a long connection
3) Fragmented HTTP Flood
Fragmented HTTP Flood
- 在这个攻击示例中,具有有效 IP 的 BOT 被用来与网络服务器建立有效的 HTTP 连接。然后,HTTP 数据包被机器人分割成小片段,并在超时前尽可能慢地发送到目标。通过这种方法,攻击者可以长时间保持连接活动,而不会向任何防御机制发出警报。
- 攻击者可以使用一个 BOT 启动多个未被发现的、长时间的和消耗资源的会话。Apache 等常用网络服务器没有有效的超时机制。这是一个 DDoS 安全漏洞,只要利用几个 BOT,就能阻止网络服务;
- 特点:
- Establish a valid HTTP connection
- Split HTTP packets into tiny fragments
- Send fragments to the target as slowly as it allows before it times out
keep a resource-consuming connection active for a long time
- 解决:
- 限制每个连接的最大持续时间
- 使用防火墙过滤器来阻止恶意流量
- 使用负载均衡器来分散流量
- 对系统进行优化,以提高其处理能力,如增加 CPU、内存等
4) Payment DDoS
Payment DDoS
- 攻击者向在线支付系统发送大量虚假支付请求,从而耗尽支付系统的资源,使其无法处理合法的支付请求,给商家和消费者带来经济损失
- 攻击者常利用大量僵尸网络节点,向支付系统发送大量虚假支付请求,这些请求中包含大量无效信息,如虚假信用卡信息、虚假支付金额等。但是,由于支付系统需要验证每个支付请求,这些无效信息会耗尽支付系统的资源,使其无法处理合法的支付请求
- 特点:
- low rate at each merchant
- high rate at acquiring bank
- 解决:商家和支付系统可以使用防欺诈系统来检测和阻止虚假支付请求、使用防火墙过滤器来阻止恶意流量、加强用户身份验证等
Asymmetric DDoS Attack (Others)👀
inside or outside the network
1) Tail Attack
bring down the entire server so far weakest link from inside
Tail Attack
- Tail Attack 利用新发现的 N 层网络应用程序的系统漏洞(亚秒级持续时间的百万瓶颈和强依赖性的资源争夺)
- 分布式节点间具有强烈依赖性毫秒级瓶颈和资源争夺,以达到攻击目的
- 最终目标是造成目标网络应用的长尾延时(如 95百分位数的响应时间 > 1 s),破坏服务提供商的长期业务,而所有的系统资源都远未达到饱和
- Tail attacks on n-tier web applications
- Identify weakest link across tiers
2) SDN CrossPath Attack
bring down the entire server so far weakest link from outside
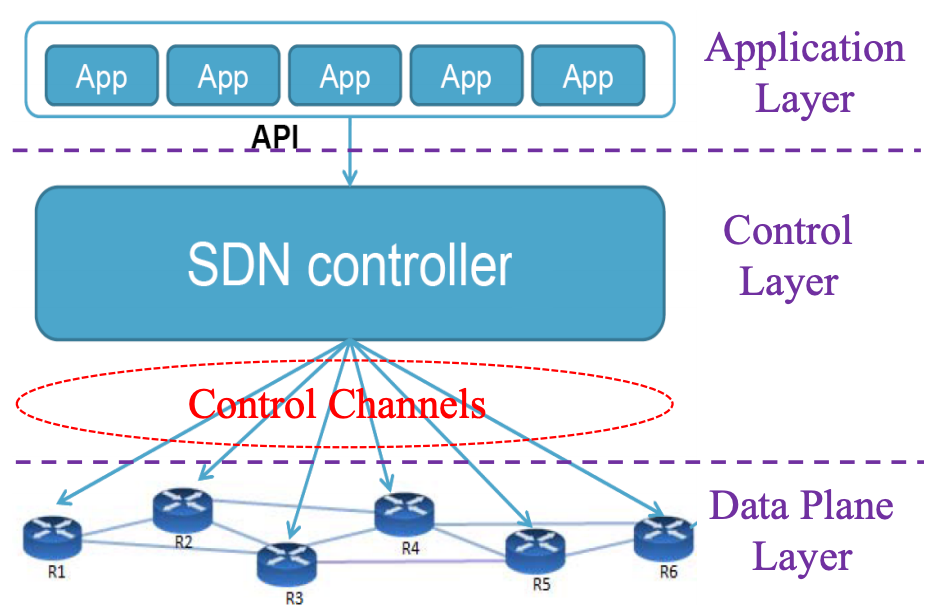
Three-Layer Architecture
- deliver all control traffic;
- issue rules from controller to switches(交换机);
- report stats from switches to controller;
-
guarantee security and reliability;
-
发现需要很多从 controller 到 switch 的直接链路,从而导致 limited scalability
- 可以使用 shared links (relay control traffic via data paths) 来解决这个问题
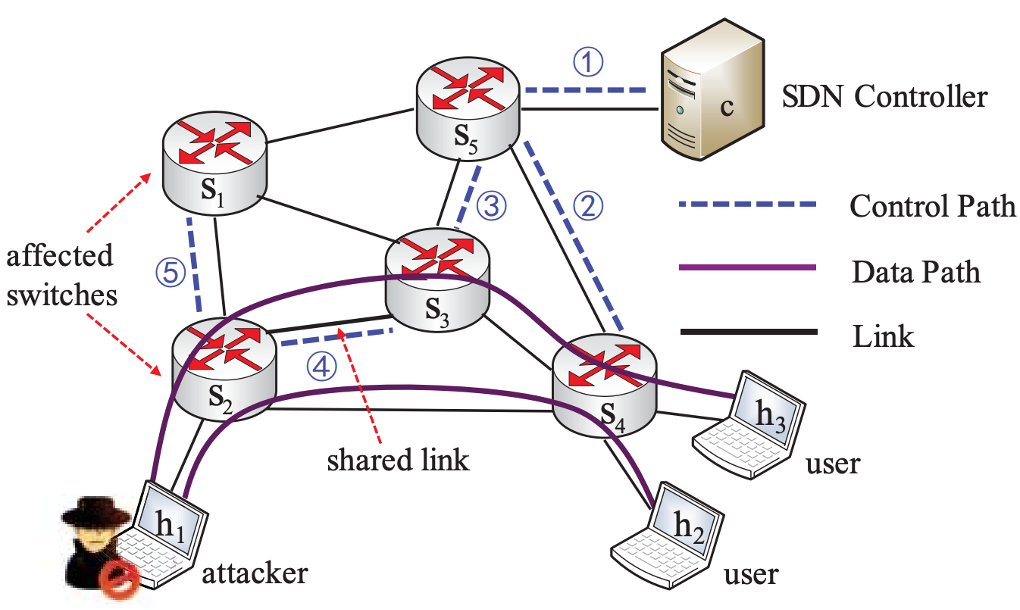
SDN CrossPath Attack
- SDN (Software Defined Networking) 是一种基于控制平面 (Control Plane) 和数据平面 (Data Plane) 分离的网络架构,它允许网络管理员通过集中式控制器来管理和控制整个网络
- SDN CrossPath Attack 是针对 SDN 中的跨路径流规则进行攻击
- 在 SDN 中,跨路径流规则用于在不同交换机间实现数据流的路由,攻击者可以利用这一点,通过向 SDN 控制器发送大量虚假流规则(这些流规则可能导致数据流跨越不同交换机路径,形成环路,数据流遇到这个环路时会陷入无限循环,占用网络带宽和交换机资源),使 SDN 控制器的资源耗尽,无法处理合法的流规则请求
特点:
- Disrupt SDN control channel via shared links
- Do not directly attack SDN controller
- Instead, block control messages with attacking traffic →
DDoS Defenses👀
DDoS Defenses
make server harder to be attacked
Type One👀
Type One
- enrich server with more resources | 通过增加服务器的资源来增强服务器的抵抗能力
- leverage the sources of others | 利用他人的资源
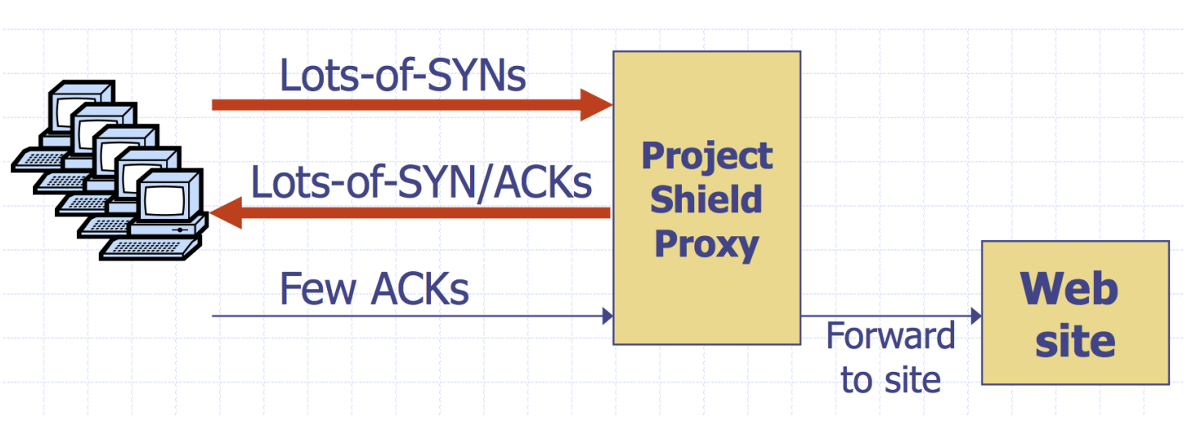
Google Project Shield
- Use Google bandwidth to shiel vulnerable websites | 使用谷歌带宽屏蔽易受攻击的网站
Type Two👀
Type Two
detect and filter attack traffic with spoofed IP addresses | 检测和过滤具有伪造 IP 地址的攻击流量
让攻击者攻击更困难
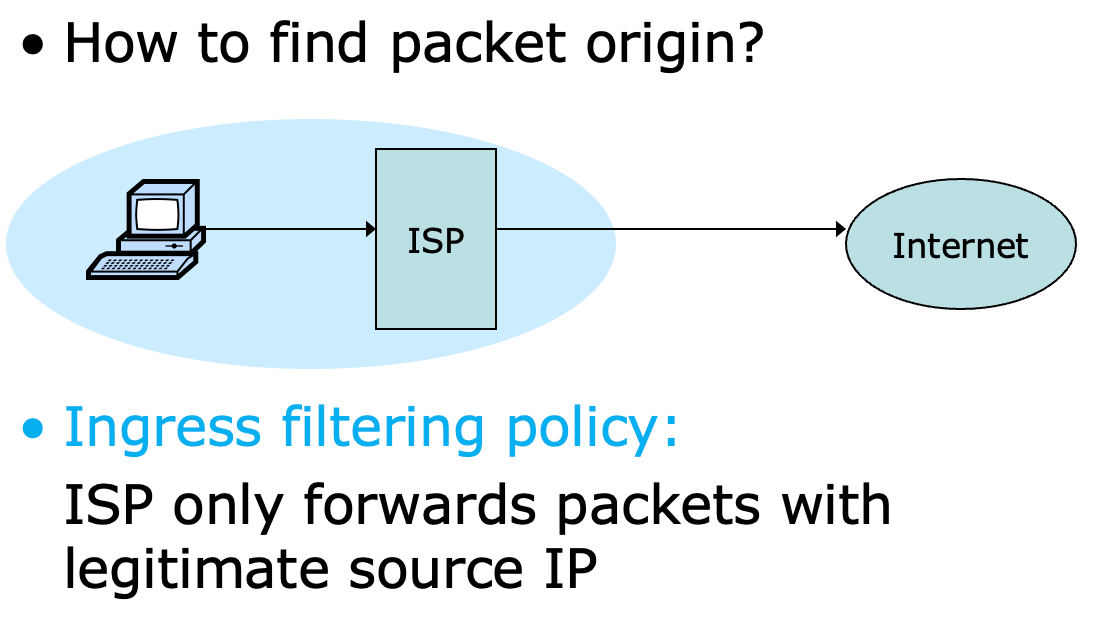
Ingress Filtering👀
Ingress Filtering
- Ingrees Filtering (入口过滤) 用于在网络入口处对数据包进行过滤和检查,通过检查网络流量的源 IP 地址,对非法的源 IP 地址进行过滤,从而阻止攻击者通过 IP Spoofing 攻击网络
- Ingress Filtering 通常部署在网络边界(如路由器,防火墙等),对网络流量进行检查和过滤,如果源 IP 地址非法,会拒绝该数据包的进入,并向管理员发出警报
- Ingress Filtering 可以有效防止 IP Spoofing 攻击,但不能完全解决网络安全问题,攻击者可以通过其他方式进行攻击
数据包通过 ISP 进入 internet, 所以要做 Ingress Filtering, 需要 ISP 的只传输合法的数据包
But → Implementation challenges:
- All ISPs need to do this – requires global cooperation
- 即便有 10% 的网络不实施,就相当于没有防御措施
- 但 ISP 没有实施的动力 – 这对他们没有影响
- As of 2017 (from CAIDA):
- 33% of autonomous systems allow spoofing;
- 23% of announced IP address space allow spoofing;
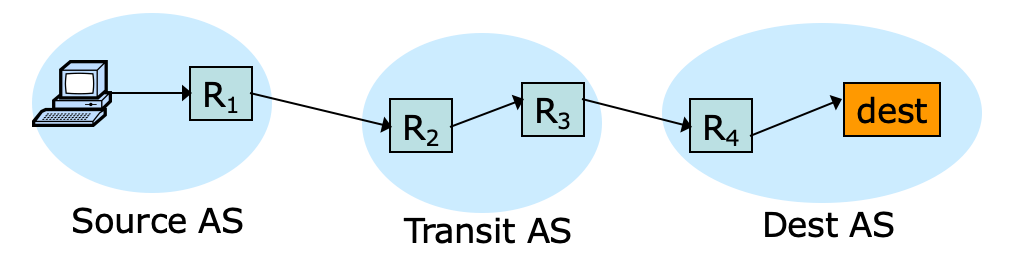
Can transit AS verify packet origin?
- 不可以,因为 routing protocols 只在乎 destination IP address
- 除非我们修改 routing protocols → 请继续阅读下面的内容
Traceback👀
Traceback
- 给定一组攻击数据包,确定到源的路径
- 最简单的方式是在数据包中维护路径信息,但这样会增加数据包的大小,降低网络性能
- 可以通过 Edge Sampling (基于路由器可信,包足够多,路由稳定的假设)
- Goal: given set of attack packets, determine path to source
- How: change routers to record info in packets
- Assumptions:
- trusted routers
- sufficient packets to track
- stable route from attacker to victim
1) 可以选择 Write path into packets (router adds its own IP address to packet victim reads path from packet)
- Limitations:
- requires space in packet
- path can be long
- no extra fields in current IP format (changes to packet format too much to expect)
- 攻击者可以轻易修改保存在数据包中的路径信息
针对 packet 过大的 limitation, 可以 Sample and Merge 的思想
- store one link in each packet;
- router probabilistically stores own address;
- fixed space regardless of path length;
由此引出 Edge Sampling
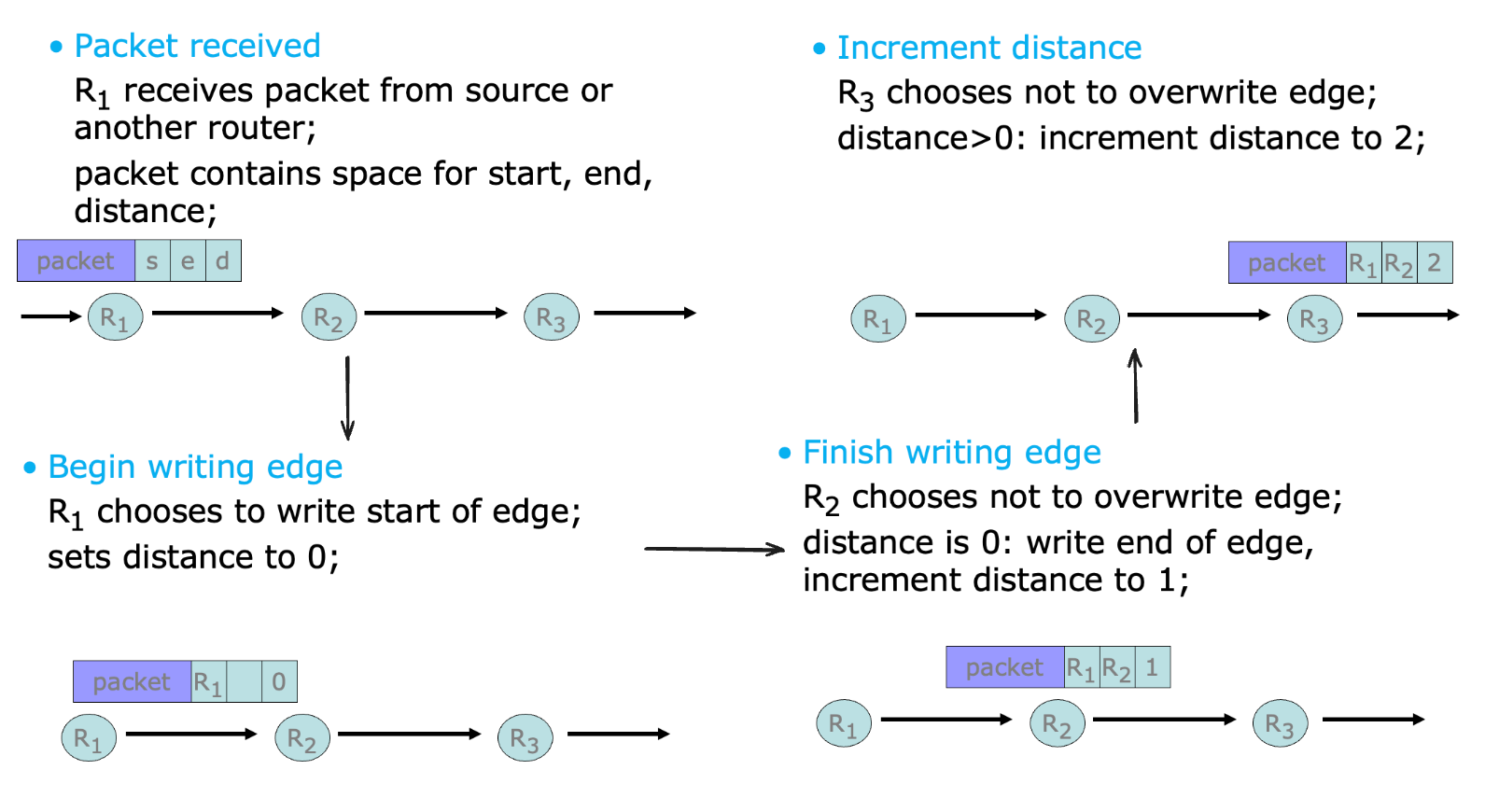
2) Edge Sampling: fileds into packet
- edge:
startandendIP addresses - distance: number of hops since edge stored
procedure 如下:
- 有一定概率改写
- 由于包足够多,因此根据不同包的采样就可以还原出路径。
- 但如果有恶意的中间路由器,就会改写这些信息,因此这个方法并不是十分有效
- 可以增加一些密码学手段做校验 (Path Validation)
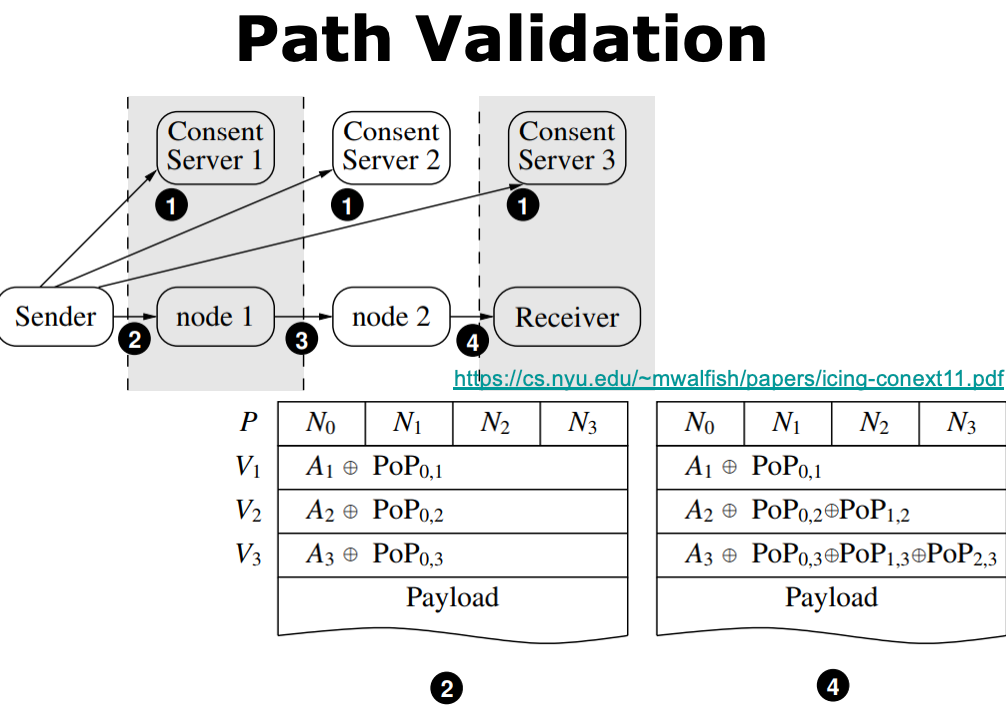
Path Validation👀
- PoC: Proof of Consent
- certify the provider’s consent to carry traffic along the path | 证明提供商同意沿该路径传输流量
- PoP: Proof of Provenance
- allow upstream nodes to prove to downstream nodes that they carried the packet | 允许上游节点向下游节点证明他们携带了数据包
每一个节点都需要给后面的每一跳提供一个凭证 —— \(O(N^2)\)
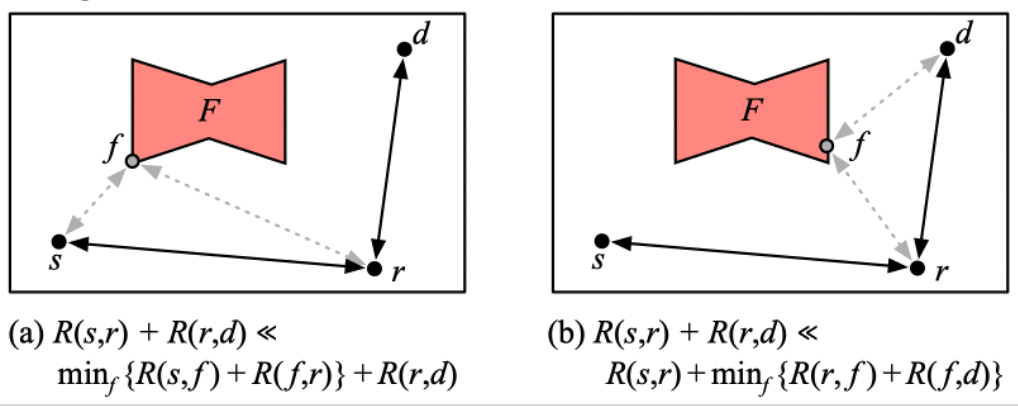
Alibi Routing👀
不希望流量经过不安全的 AS
AliBi Routing
- AliBi Routing 是一种网络路由安全技术,旨在保护互联网路由协议(如 BGP)中的路由信息不被攻击者篡改或伪造
- AliBi Routing 通过在网络中添加一组辅助路径来实现路由验证和错误检测
- 辅助路径由可信第三方提供,与主路径并行传输路由信息
如何证明一个 packet 没有经过某个 AS? -> proof waypoint
proof waypoint : packet 在给定时间限制内不可能同时经过 proof waypoint 和需要避开的 AS
- s: source
- d: destination
- F region: AS to avoid
- r: proof waypoint
如上图,思路就是选取一个特别的点,如果走的时间比这个更长,就说明这个点位于 F region
Type Three👀
Type Three
cost more resources from attacker
消耗攻击者更多资源
Client Puzzles👀
Client Puzzles
让 client (attackers) 算 puzzle
- Idea:
- force every client to do moderate amount of work for every connection they make
- EXample:
- server sends: C
- client: given challenge C find X s.t.
- \(\text{LSB}_n\text{(SHA-1(C||X))} = \text{0}^n\)
- Benfits:
- 在检测到攻击时调用
- 可根据攻击流量调整 n
- Limitations
- require changes to protocols, clients, and servers;
- during attack, hurts low-power legitimate clients (e.g., phones);
CAPTCHA👀
CAPTCHA
- CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart)
- challenge–response test used in computing to determine whether or not the user is human
- 就是验证码 (Type: Text, Image, Audio…)
- Vulnerable to auto-identification
-
Timeout: evict a backlog entry if no ack is received until timeout, e.g., 3 mins ↩