Backtracking👀
约 474 个字 44 行代码 预计阅读时间 2 分钟
Rationale
- 解决问题的一个可靠的方法是列出所有候选答案,检查每个答案,然后在所有或部分候选答案被检查之后,宣布确定的答案。
- 如果候选者有限且不是特别多的话,是可以在检查后确定答案的。
- 而 backtracking | 回溯法 使我们能够消除对大量候选子集的显式检查,同时仍然保证如果算法运行到终止时能找到答案。这种方法其实就是 pruning | 剪枝 思想。
basic idea
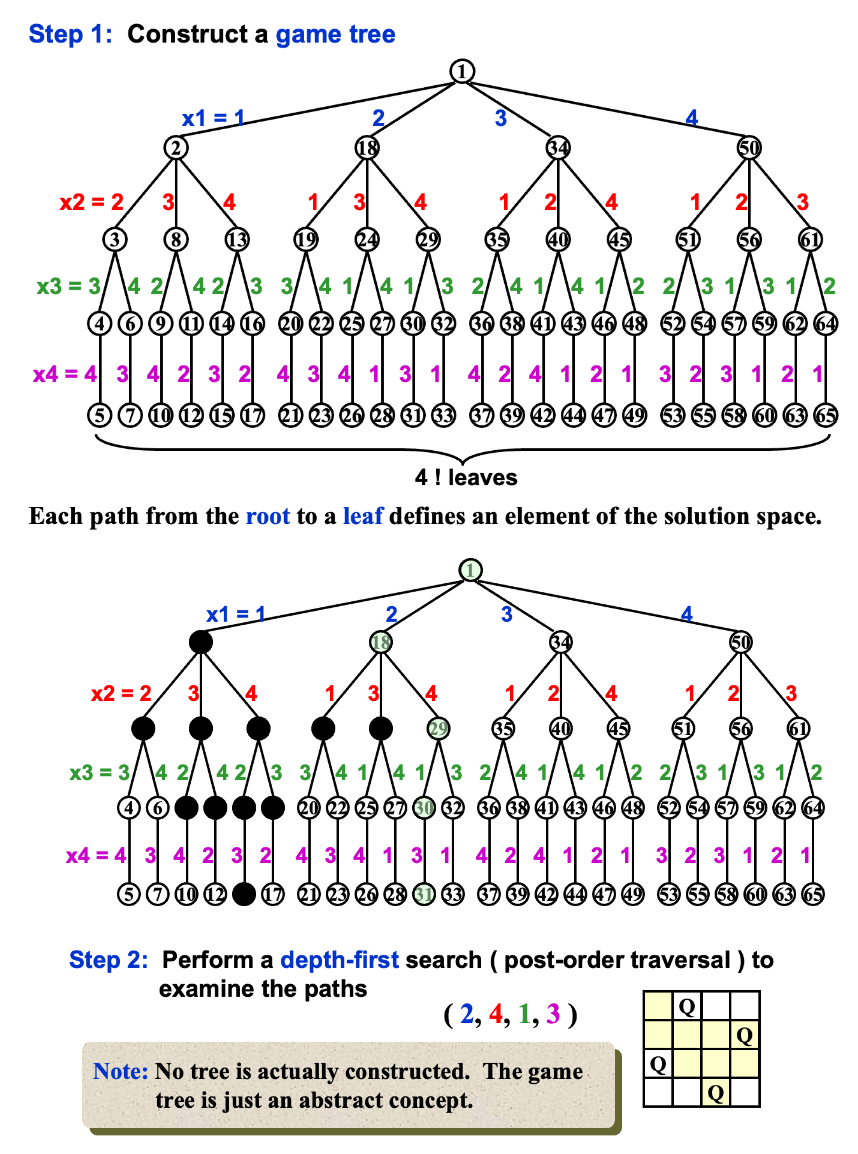
- Suppose we have a partial solution \((x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_i)\), where each \(x_k \in S_k\) for \(1 \leq k \leq i < n\).
- First we add \(x_{i+1} \in S_{i+1}\) and check if the new solution \((x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_{i+1})\) satisfies the constraints.
- If the answer is “yes”, we continue to add the next \(x\), else we delete \(x_i\) and backtrack to the previous partial solution \((x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_{i-1})\).
DFS + purning = backtracking
下面,由一些经典问题来引入回溯法的基本思想。
Eight Queens Problem👀
Problem
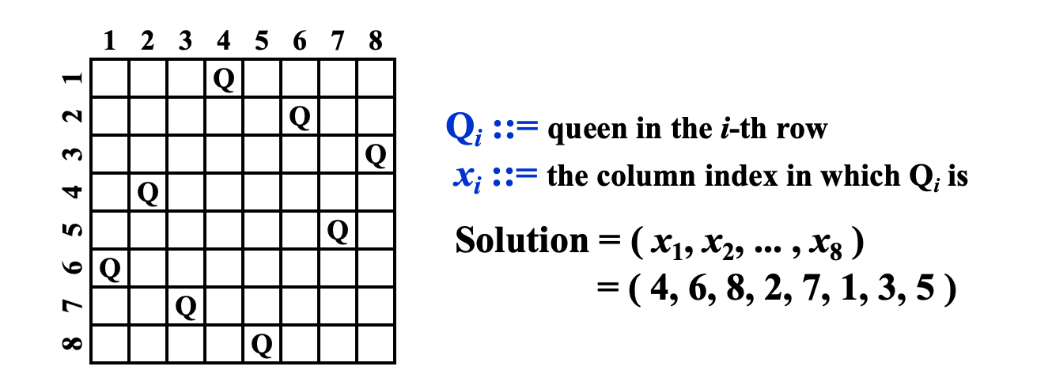
- 在 8 \(\times\) 8 格的国际象棋上摆放 8 个 queen,使其不能互相攻击
- 即任意两个皇后都不能处于同一行、同一列或同一斜线上,问有多少种摆法。
例如其中一种解法如下:
该问题的 Constraints 如下:
- \(S_i = \{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8\}\) for \(1 \leq i \leq 8\)
- \(x_i \neq x_j\) if \(i \neq j\)
- \((x_i - x_j) / (i - j) \neq \pm 1\) if \(i \neq j\)
- 其实,这个问题的 Constraints 第一个暗示解空间有 \(8^8\) 种可能
- 问题的第二条约束条件暗示了解空间的大小缩减为为 \(8!\) 种可能
Turnpike problem👀
- For every d remaining in D, at least one of its endpoints is not determined
- For maximum d remaining in D, at least one of its endpoints is a0 or an-1
bool Reconstruct(DistType X[ ], DistSet D, int N, int left, int right)
{
/* X[1]...X[left-1] and X[right+1]...X[N] are solved */
bool Found = false;
if ( Is_Empty( D ) ) return true; /* solved */
D_max = Find_Max( D ); /* option 1:X[right] = D_max */
/* check if |D_max-X[i]|D is true for all X[i]’s that have been solved */
OK = Check( D_max, N, left, right ); /* pruning */
if ( OK ) {
/* add X[right] and update D */
X[right] = D_max;
for ( i=1; i<left; i++ )
Delete( |X[right]-X[i]|, D);
for ( i=right+1; i<=N; i++ )
Delete( |X[right]-X[i]|, D);
Found = Reconstruct ( X, D, N, left, right-1 );
if ( !Found ) {
/* if does not work, undo */
for ( i=1; i<left; i++ )
Insert( |X[right]-X[i]|, D);
for ( i=right+1; i<=N; i++ )
Insert( |X[right]-X[i]|, D);
}
} /* finish checking option 1 */
if ( !Found ) { /* if option 1 does not work */
/* option 2: X[left] = X[N]-D_max */
OK = Check( X[N]-D_max, N, left, right );
if ( OK ) {
X[left] = X[N] – D_max;
for ( i=1; i<left; i++ )
Delete( |X[left]-X[i]|, D);
for ( i=right+1; i<=N; i++ )
Delete( |X[left]-X[i]|, D);
Found = Reconstruct (X, D, N, left+1, right );
if ( !Found ) {
for ( i=1; i<left; i++ )
Insert( |X[left]-X[i]|, D);
for ( i=right+1; i<=N; i++ )
Insert( |X[left]-X[i]|, D);
}
} /* finish checking option 2 */
} /* finish checking all the options */
return Found;
}
- worst case: O(2n) (rare)
- best case: O(n) (most instances)
Game - Tic-Tac-Toe👀
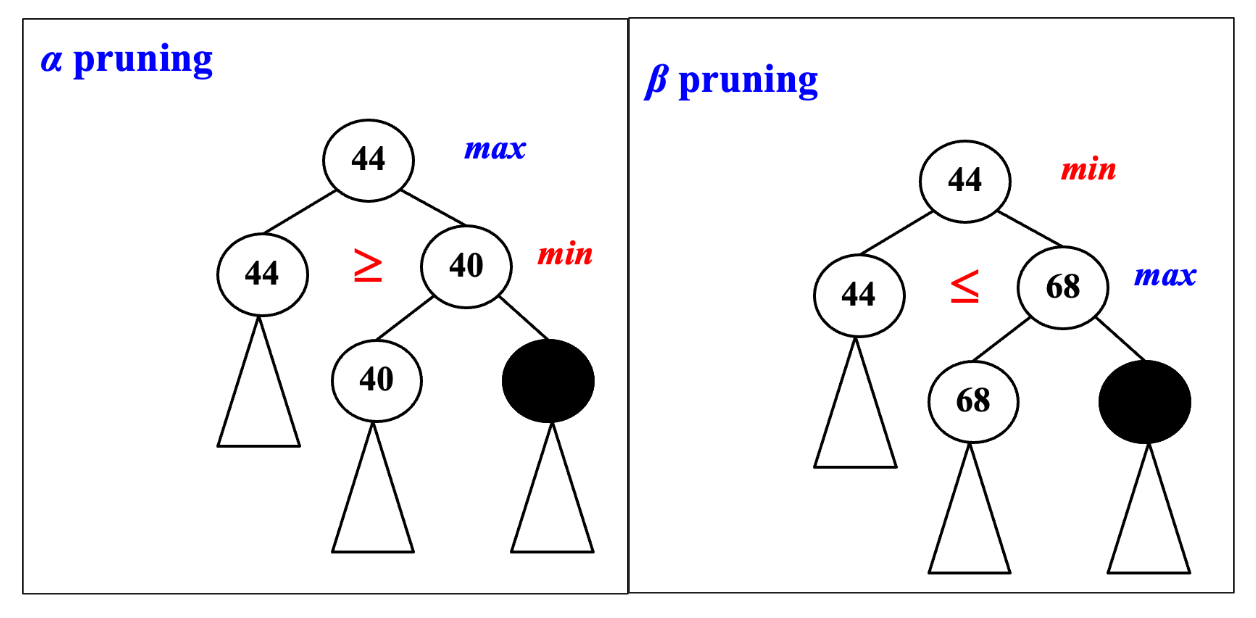
Pruning👀
不管树中黑色节点的值是多少,都没有意义
\(\alpha-\beta\) pruning: when both techniques are combined. In practice, it limits the searching to only \(O(\sqrt{N})\) nodes, where N is the size of the full game tree.
本文总阅读量:
次